[toc]
Poker Algorithm developer history
论文阅读《Regret minimization in games and the development of champion multiplayer computer poker playing agents》(游戏中的遗憾最小化与多人计算机扑克游戏冠军的发展)
Definition
Definition 2.1 normal-form game

Definition 2.1. A finite normal-form game G is a tuple <N, A, u> containing the following components:
- A finite set N = {1, 2, …, n} of players.
- A set of action profiles A = A1×A2×· · ·×An, with Ai being a finite set of actions available to player i.
- For each i 2 N, a utility function ui : A ! R that denotes the payoff for player i under each possible action profile
Definition 2.2 Extensive-form game

Definition 2.3 perfect reall & imperfect recall
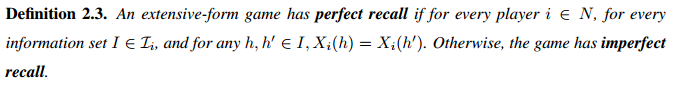
Definition 2.4 纳什均衡
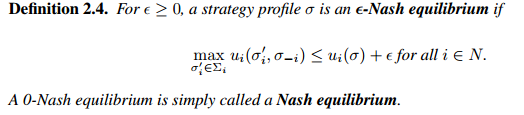
Definition 2.5 Weakly/strictly dominated stregy

在三人博弈中,纳什均衡的计算是属于PPAD-complete的Computing Nash Equilibrium (二人博弈也属于此)
Nash Equilibrium 两个推广
PDF_correlated equilibria()
- no player has an incentive to unilaterally deviate from any recommendation
PDF_coarse correlated equilibria
Definition 2.6 abstraction for player


Definition2.7 Grafting partition for player i
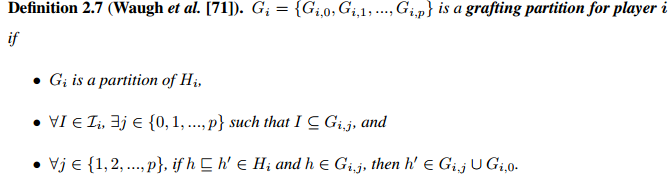
Definition2.8 grafted strategy for player i
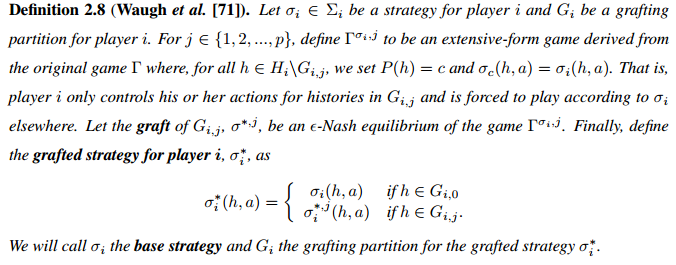
Theorem
Theorem2.1 2e-Nash equilibrium
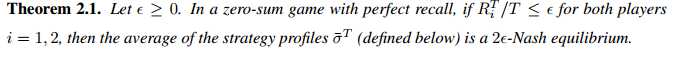
Theorem2.2 regret & step
当使用regret matching时,玩家regret与step的平方根成正比
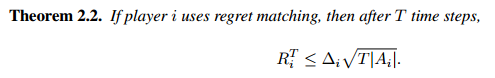
Theorem2.3 regert max
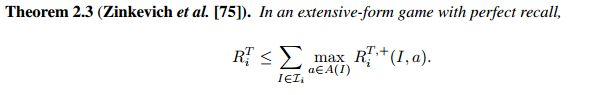
Theorem2.4 平均regret bounded
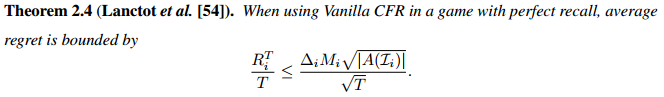
Algorithm Method
Regret Matching
accumulated regret: 衡量玩家i有多少次,宁愿选择a,而不跟随σ
$$
R_i^T (a) = \sum_{t=1}^{T} (u_i(a, σ_{-i}^t) - u_i(σ_i^t, σ_{-i}^t)
$$
Successive strategies:
$$
\sigma_i^{T+1}(a) = \frac{R_i^{T,+}(a)}{\sum_{b \in A_i}R_i^{T, +}(b)}
$$
Counterfactual Regret Minimization(CFR)
counterfactual value (player i)
$$
u(i, \sigma) = \sum_{z\in Z_I} u_i(z)\pi_{-1}^\sigma (z[I])\pi^{\sigma}(z[I], z)
$$
counterfactual regret (at iteration t)
$$
r_i^t(I,a ) = v(I, \sigma_{I \to a} ^ t) - u_i(I, \sigma^t)
$$
σ(I->a) is the profile σ except at I, action a is always taken.
the regret $r_i^t(i; a) $ measures how much player i would rather play action a at i than follow σt i at i, assuming player i plays to reach i.
后悔 $r_i^t(i; a) $ 衡量的是,我宁愿在I上玩动作a,也不愿在I上跟随σ_i^t,假设Player玩到I。
cumulative counterfactual regret
$$
R_i^T (I, a) =\sum_{t=1}^{T}r_i^t(I, a)
$$
current strategy profile
$$
\sigma_i^{T+1}(I, a) = \frac{R_i^{T,+}(I, a)}{\sum_{b \in A(I)}R_i^{T, +}(I, b)}
$$
MCCFR
Chance Sampling(CS)
sampled counterfactual value
$$
\widetilde{u}i(I, \sigma) = \sum{z\in Z_I \cap Q_j} u_i(z)\pi_{-i}^{\sigma}(z[I]) \pi^{\sigma} (z[I], z)/q(z)
$$
sampled counterfactual regret
$$
\widetilde{r}_i^t(I, a) = \widetilde{v}i(I, \sigma{I \to a}^t) - \widetilde{v}_i(I, \sigma^t)
$$
sampled cumulative counterfactual regret
$$
\widetilde{R}_i^T = \sum _{t=1}^{T}\widetilde{r}_i^t(I, a)
$$
External Sampling(ES)
ES takes CS one step further by considering only a single action for not only chance, but also for the opponents, where opponent actions are sampled according to the current profile $σ_{-i}^t $
Outcome Sampling(OS)
最极端的mccfr版本,
samples a single action at every history, walking just a single trajectory through the tree on each traversal ($Q_j = {z}$). 在每一段历史记录中对单个动作进行采样,每次遍历时只遍历一条轨迹($Q_j = {z}$)。
CS-MCTS
ES-MCTS Pesudocode
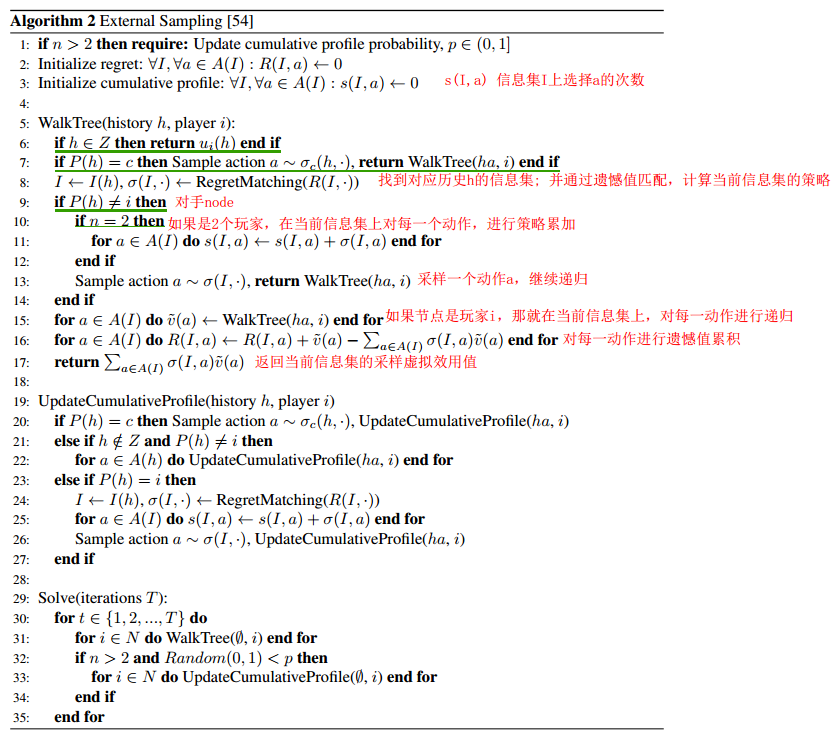
WalkTree (recursive function)
four case:
-1 reached teminal node : 返回效用值;(line 6)
-2 at a chance node : 根据策略采样一个动作,并续递归;(line 7)
-3 at opponent’s chance node : 采样个动作,并继续递归.(line 9-14)
-4 update the cumulative profile (in two player game;)
ES:递归方法WakeTree
UpdateCumulativeProfile
after walkTree
Probing + MCCFR
Pesudocode

对比ES算法,多了一个action set sampling distribution Q(I), 对于已经
0:walk tree(h, i, q):
1、h是terminal节点,返回u
2、P(h)是chanceNode,sample action $a \sim \sigma_c(h,·)$, goto_0(ha)
3、P(h)是 opponent’s Node,
3.1、对所有的$a \in A(I)$更新$s(I,a) = s(I, a) + (\sigma(I, a)/q)$
3.2、sample action $a \sim \sigma(I, ·)$, goto_0(ha)
采样信息集$Q(I) \sim Q(I)$
4、遍历玩家i在当前信息集I上的所有可能action
- 如果 a 属于Q(I): 更新q’并且goto_0(ha)
- 否则:Probe(ba)
5、便利i的信息I下所有可能action,更新R(I, a)
6、返回信息集上累计采样虚拟效用值$\sum_{a \in A(I)} \sigma(I, a) \widetilde{u}(a)$
AS-MCTS(Average Strategy Sampling)
AS can be seen as a sampling scheme between OS and ES (可看作OS, ES之间的折中方案)
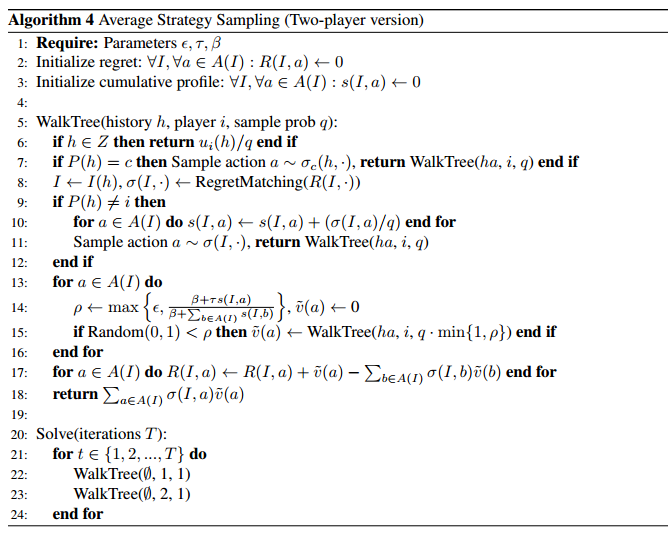
AS_select:
AS对每个信息集上玩家的action子集采样。而不像OS采样一个action,也不像ES采样所有action
cumulative profile $s^T_i(I, ·) $on iteration T , an exploration parameter $\epsilon \in (0, 1]$,a threshold parameter $τ \in [1, 1)$, and a bonus parameter $β \in [0, 1)$, each of player i’s actions $a \in A(I)$ are sampled independently with probability :
$$
ρ(I; a) = max {\epsilon, \frac{β + \tau s_i^T(I, a)} {\beta + \sum_{b \in A(I)} s^T_i(I, b)} }
$$
[GO](#Regret Matching)
Reference
《Regret minimization in games and the development of champion multiplayer computer poker playing agents》(游戏中的遗憾最小化与多人计算机扑克游戏冠军的发展)