DensePose citations:
[TOC]
应用场景:
单张图片的人脸三维建模: 11,
密集人脸对齐方面: 8,11,
Human DensePose Estimation:4, 7,9
Hand 三维建模: 10
三维形状建模:5,
三维物体的深度姿态估计: 6,
密集人脸对齐:
人脸对齐这项技术的应用很广泛,比如自动人脸识别,表情识别以及人脸动画自动合成等
密集人脸对齐算法将人脸图像匹配到一个最佳的3D人脸模型上,这些3D人脸模型中包含数以千计的特征点,从而实现了密集的人脸对齐。但是我们仍然面临两个问题:目前基于3D人脸模型匹配的人脸对齐算法仅仅利用稀疏的特征点来构造,如果要实现高质量的密集人脸对齐(DeFA),面临的首要问题就是没有相应的训练数据库,所有的人脸对齐数据库中标记的特征点都不超过68个特征点,所以我们需要寻找有用的信息来作为额外的限制条件,并将这些信息嵌入到学习框架中。面临的第二个问题就是需要各种的训练数据,但是不同的人脸对齐数据库标记的特征点个数不一样。
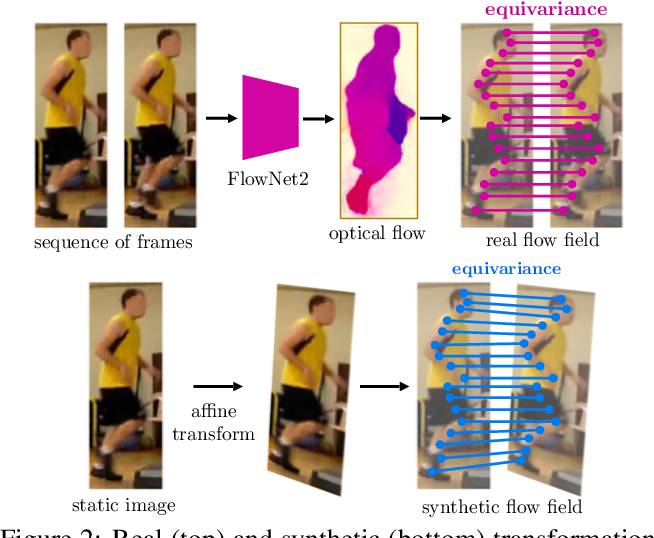
1. Slim DensePose: Thrifty Learning from Sparse Annotations and Motion Cues
《Slim DensePose:从稀疏的注释和动作线索中学习》
- CVPR 2019 semanticscholar
DensePose将图像像素密集地映射到人体表面坐标,从而取代了传统的地标探测器。然而,这一功能大大增加了注释时间,因为管理模型需要为每个pose实例手动标记数百个点。因此,在这项工作中,我们寻找方法来显著地精简DensePose注释,从而提出更有效的数据收集策略。特别地,我们证明如果在视频帧中收集注释,它们的效果可以通过使用动作线索免费倍增。为了探索这个想法,我们引入了DensePose- track,这是一个视频数据集,其中选择的帧以传统的DensePose方式进行注释。然后,基于密度映射的几何特性,利用视频的动态特性及时传播地面真值注释,并学习暹罗等方差约束。在对各种数据注释和学习策略进行了详尽的经验评估之后,我们证明这样做可以在强基线上提供显著改进的姿态估计结果。然而,尽管最近的一些研究表明,仅仅通过对孤立的帧应用几何变换来合成运动模式的效果要差得多,而从视频中提取运动线索的效果要大得多。
2. BodyNet: Volumetric Inference of 3D Human Body Shapes
《BodyNet:三维人体形状的体积推理》
- ECCV 2018 semanticscholar
Human shape estimation is an important task for video editing , animation and fashion industry. Predicting 3D human body shape from natural images, however, is highly challenging due to factors such as variation in human bodies, clothing and viewpoint. Prior methods addressing this problem typically attempt to fit parametric body models with certain priors on pose and shape. In this work we argue for an alternative representation and propose BodyNet, a neural network for direct inference of volumetric body shape from a single image. BodyNet is an end-to-end trainable network that benefits from (i) a volumetric 3D loss, (ii) a multi-view re-projection loss, and (iii) intermediate supervision of 2D pose, 2D body part segmentation, and 3D pose. Each of them results in performance improvement as demonstrated by our experiments. To evaluate the method, we fit the SMPL model to our network output and show state-of-the-art results on the SURREAL and Unite the People datasets, outperforming recent approaches. Besides achieving state-of-the-art performance, our method also enables volumetric body-part segmentation.
人体形态估计是视频编辑、动画制作和时尚产业的一项重要工作。然而,从自然图像中预测三维人体形状,由于人体、服装和视角的变化等因素,具有很高的挑战性。解决这一问题的先前的方法通常试图将参数化的身体模型与特定的姿态和形状进行拟合。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种替代的表示方法,并提出了BodyNet,这是一种神经网络,可以直接从单个图像推断出身体的体积形状。BodyNet是一个端到端可训练的网络,它受益于(i)体三维损失,(ii)多视图再投影损失,和(iii)中间监督2D位姿,2D身体部分分割,和3D位姿。实验结果表明,每一种方法都能提高系统的性能。为了对该方法进行评估,我们将SMPL模型与我们的网络输出相匹配,并在SURREAL数据库上显示最新的结果,并将人员数据集统一起来,从而优于最近的方法。除了实现最先进的性能,我们的方法还可以实现体块分割。

3. Synthesizing facial photometries and corresponding geometries using generative adversarial networks
《利用生成对抗性网络合成人脸照片和相应的几何图形》
- TOMM 2019
Artificial data synthesis is currently a well studied topic with useful applications in data science, computer vision, graphics and many other fields. Generating realistic data is especially challenging since human perception is highly sensitive to non-realistic appearance. In recent times, new levels of realism have been achieved by advances in GAN training procedures and architectures. These successful models, however, are tuned mostly for use with regularly sampled data such as images, audio and video. Despite the successful application of the architecture on these types of media, applying the same tools to geometric data poses a far greater challenge. The study of geometric deep learning is still a debated issue within the academic community as the lack of intrinsic parametrization inherent to geometric objects prohibits the direct use of convolutional filters, a main building block of today’s machine learning systems. In this paper we propose a new method for generating realistic human facial geometries coupled with overlayed textures. We circumvent the parametrization issue by imposing a global mapping from our data to the unit rectangle. This mapping enables the representation of our geometric data as regularly sampled 2D images. We further discuss how to design such a mapping to control the mapping distortion and conserve area within the mapped image. By representing geometric textures and geometries as images, we are able to use advanced GAN methodologies to generate new geometries. We address the often neglected topic of relation between texture and geometry and propose to use this correlation to match between generated textures and their corresponding geometries. In addition, we widen the scope of our discussion and offer a new method for training GAN models on partially corrupted data. Finally, we provide empirical evidence demonstrating our generative modelâĂŹs is ability to produce examples of new identities independent from the training data while maintaining a high level of realism, two traits that are often at odds.
人工数据合成是当前研究的热点,在数据科学、计算机视觉、图形学等诸多领域有着广泛的应用。生成真实的数据尤其具有挑战性,因为人类感知对非真实的外观高度敏感。近年来,随着GAN培训程序和体系结构的进步,现实主义达到了新的水平。然而,这些成功的模型主要针对图像、音频和视频等定期采样的数据进行了调优。尽管在这些类型的媒体上成功地应用了架构,但在几何数据上应用相同的工具带来了更大的挑战。几何深度学习的研究在学术界仍然是一个有争议的问题,因为几何对象缺乏固有的参数化,因此无法直接使用卷积滤波器,而卷积滤波器是当今机器学习系统的主要组成部分。在这篇论文中,我们提出了一种新的方法来生成具有叠加纹理的真实的人脸几何图形。我们通过将数据映射到单元矩形来避免参数化问题。这种映射使我们的几何数据表示为定期采样的2D图像。我们进一步讨论了如何设计这样一个映射来控制映射失真和保留映射图像中的区域。通过将几何纹理和几何图形表示为图像,我们能够使用高级GAN方法生成新的几何图形。**我们解决了纹理和几何之间经常被忽视的问题,并建议使用这种相关性来匹配生成的纹理和它们相应的几何图形。**此外,我们扩大了讨论的范围,并提供了一种新的方法来训练GAN模型对部分损坏的数据。最后,我们提供了经验证据证明生成modelaĂŹs能力产生新的身份独立于训练数据的例子,同时保持高水平的现实主义,这两个特征常常相左。
4. Adaptive Multi-Path Aggregation for Human DensePose Estimation in the Wild
《自适应多路径聚合技术在野外进行人体密度估计》
Dense human pose “in the wild’’ task aims to map all 2D pixels of the detected human body to a 3D surface by establishing surface correspondences, i.e., surface patch index and part-specific UV coordinates. It remains challenging especially under the condition of “in the wild’’, where RGB images capture complex, real-world scenes with background, occlusions, scale variations, and postural diversity. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end deep Adaptive Multi-path Aggregation network (AMA-net) for Dense Human Pose Estimation. In the proposed framework, we address two main problems: 1) how to design a simple yet effective pipeline for supporting distinct sub-tasks (e.g., instance segmentation, body part segmentation, and UV estimation); and 2) how to equip this pipeline with the ability of handling “in the wild’’. To solve these problems, we first extend FPN by adding a branch for mapping 2D pixels to a 3D surface in parallel with the existing branch for bounding box detection. Then, in AMA-net, we extract variable-sized object-level feature maps (e.g., 7×7, 14×14, and 28×28), named multi-path, from multi-layer feature maps, which capture rich information of objects and are then adaptively utilized in different tasks. AMA-net is simple to train and adds only a small overhead to FPN. We discover that aside from the deep feature map, Adaptive Multi-path Aggregation is of particular importance for improving the accuracy of dense human pose estimation “in the wild’’. The experimental results on the challenging Dense-COCO dataset demonstrate that our approach sets a new record for Dense Human Pose Estimation task, and it significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. Our code: \urlhttps://github.com/nobody-g/AMA-net
密集人体姿态“在野外”任务的目的是通过建立表面对应,将被检测人体的所有2D像素映射到3D表面,即,表面斑块指数和部分特异性UV坐标。它仍然具有挑战性,特别是在“在野外”的条件下,RGB图像捕获复杂的,现实世界的场景与背景,遮挡,尺度变化,和姿势多样性。本文提出了一种用于密集姿态估计的端到端深度自适应多路径汇聚网络(AMA-net)。在该框架中,我们解决了两个主要问题:1)如何设计一个简单而有效的管道来支持不同的子任务(如实例分割、身体部分分割和紫外线估计);2)如何使管道具备“野外”处理能力。为了解决这些问题,我们首先扩展了FPN,在现有的边界盒检测分支的基础上,加入一个用于将2D像素映射到3D表面的分支。然后,在AMA-net中,我们从多层特征图中提取可变大小的对象级特征图(如7×7、14×14、28×28),并命名为multi-path,这些特征图捕获对象的丰富信息,然后自适应地用于不同的任务。net训练简单,只增加了FPN的一小部分开销。我们发现,除了深度特征图外,自适应多路径聚合对于提高“野外”密集人体姿态估计的准确性尤为重要。在具有挑战性的Dense- coco数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法为密集人体姿态估计任务创造了新的记录,并且显著优于目前最先进的方法。我们的代码: https: / /github.com/nobody-g/AMA-net
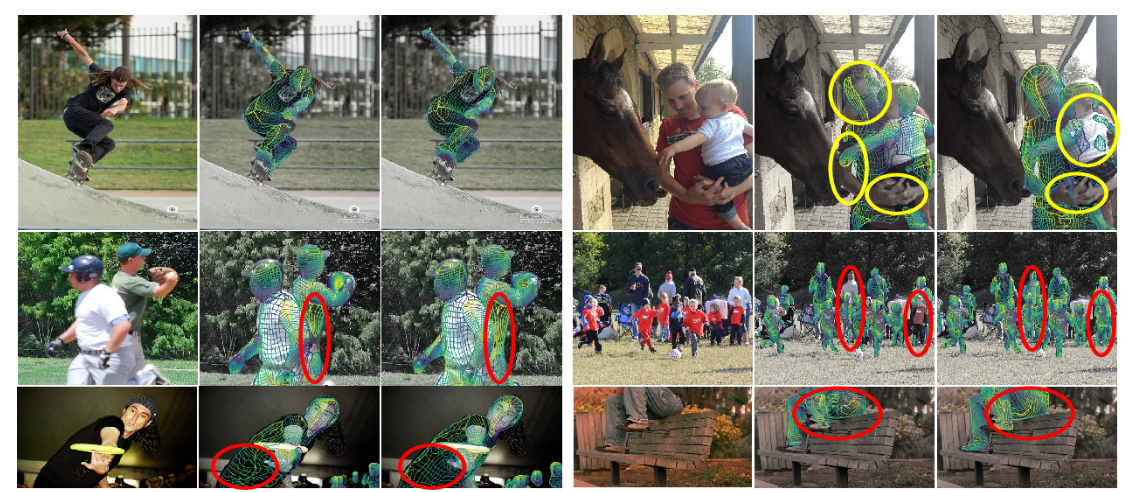

Figure 5: DensePose R-CNN vs AMA-net. Left: input image; middle: DensePose R-CNN; right: AMA-net. The red circles spot the difference between the DensePose R-CNN and AMA-net estimation. The yellow circles mark the positions where both methods fail to estimate UV coordinates.
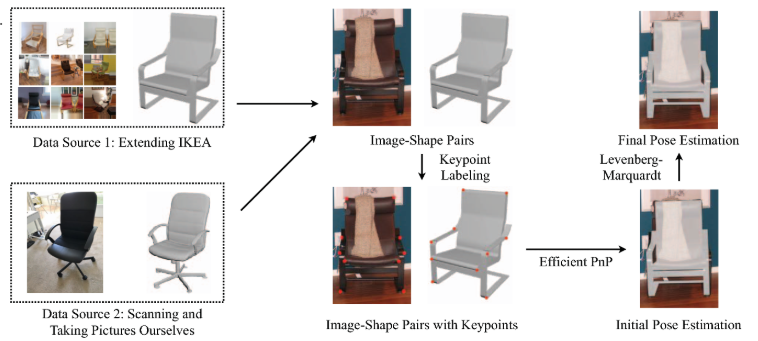
5. Pix3D: Dataset and Methods for Single-Image 3D Shape Modeling
《Pix3D:单图像三维形状建模的数据集和方法》
IEEE 2018
https://github.com/xingyuansun/pix3d
We study 3D shape modeling from a single image and make contributions to it in three aspects. First, we present Pix3D, a large-scale benchmark of diverse image-shape pairs with pixel-level 2D-3D alignment. Pix3D has wide applications in shape-related tasks including reconstruction, retrieval, viewpoint estimation, etc. Building such a large-scale dataset, however, is highly challenging; existing datasets either contain only synthetic data, or lack precise alignment between 2D images and 3D shapes, or only have a small number of images. Second, we calibrate the evaluation criteria for 3D shape reconstruction through behavioral studies, and use them to objectively and systematically benchmark cutting-edge reconstruction algorithms on Pix3D. Third, we design a novel model that simultaneously performs 3D reconstruction and pose estimation; our multi-task learning approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on both tasks.
我们研究了单一图像的三维形状建模,并在三个方面做出了贡献。首先,我们提出了Pix3D,一个大规模的基准的各种图像形状对像素级2D-3D对齐。Pix3D在形状相关的重建、检索、视点估计等方面有着广泛的应用。然而,建立如此大规模的数据集是极具挑战性的;现有的数据集要么只包含合成数据,要么缺乏二维图像和三维形状之间的精确对齐,要么只有少量图像。其次,通过行为研究对三维形状重建的评价标准进行校准,并将其用于客观、系统地对Pix3D上的前沿重建算法进行基准测试。第三,我们设计了一个可以同时进行三维重建和姿态估计的新模型;我们的多任务学习方法在两个任务上都达到了最先进的性能。
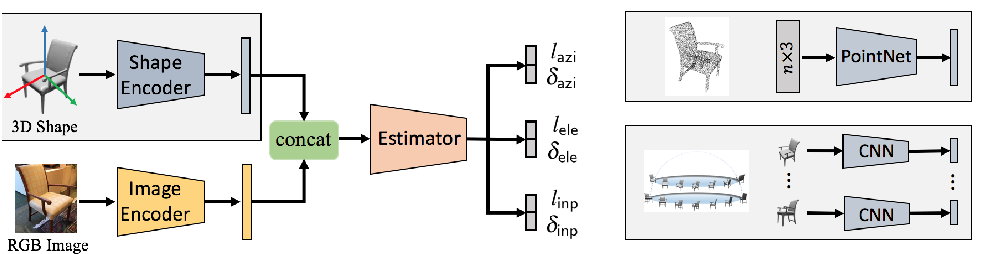
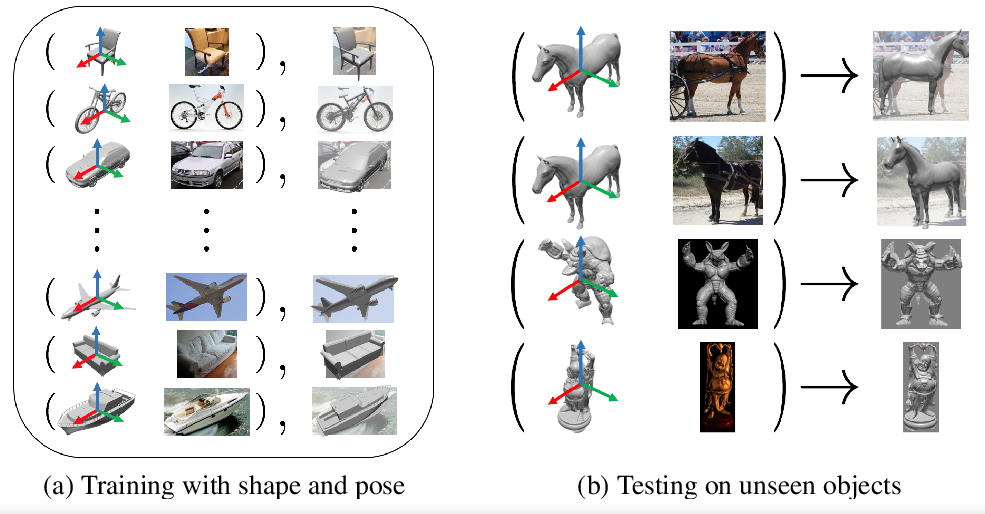
6. Pose from Shape: Deep Pose Estimation for Arbitrary 3D Objects
《形状生成姿态:任意三维物体的深度姿态估计》
Most deep pose estimation methods need to be trained for specific object instances or categories. In this work we propose a completely generic deep pose estimation approach, which does not require the network to have been trained on relevant categories, nor objects in a category to have a canonical pose. We believe this is a crucial step to design robotic systems that can interact with new objects “in the wild” not belonging to a predefined category. Our main insight is to dynamically condition pose estimation with a representation of the 3D shape of the target object. More precisely, we train a Convolutional Neural Network that takes as input both a test image and a 3D model, and outputs the relative 3D pose of the object in the input image with respect to the 3D model. Key ResultWe demonstrate that our method boosts performances for supervised category pose estimation on standard benchmarks, namely Pascal3D+, ObjectNet3D and Pix3D, on which we provide results superior to the state of the art. More importantly, we show that our network trained on everyday man-made objects from ShapeNet generalizes without any additional training to completely new types of 3D objects by providing results on the LINEMOD dataset as well as on natural entities such as animals from ImageNet.
大多数深度姿态估计方法需要针对特定的对象实例或类别进行训练。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种完全通用的深度位姿估计方法,它不需要网络对相关类别进行训练,也不需要类别中的对象具有标准位姿。我们相信,这是设计机器人系统的关键一步,它可以与“在野外”不属于预先定义的类别的新对象进行交互。我们的主要观点是用目标物体的三维形状表示动态条件位姿估计。更准确地说,我们训练了一个卷积神经网络,它以测试图像和三维模型为输入,输出输入图像中物体相对于三维模型的三维姿态。关键结果我们证明,我们的方法提高了监督类别的性能估计的标准基准,即Pascal3D+, ObjectNet3D和Pix3D,我们提供的结果优于目前的水平。更重要的是,我们通过提供LINEMOD数据集和来自ImageNet的动物等自然实体的结果,展示了我们的网络在ShapeNet的日常人造对象上的训练,而不需要任何额外的训练就可以概括为全新类型的3D对象。
7. DaNet: Decompose-and-aggregate Network for 3D Human Shape and Pose Estimation
《DaNet:用于三维人体形状和姿态估计的分集网络》
- 2019
- semanticscholar
Reconstructing 3D human shape and pose from a monocular image is challenging despite the promising results achieved by most recent learning based methods. The commonly occurred misalignment comes from the facts that the mapping from image to model space is highly non-linear and the rotation-based pose representation of the body model is prone to result in drift of joint positions. In this work, we present the Decompose-and-aggregate Network (DaNet) to address these issues. DaNet includes three new designs, namely UVI guided learning, decomposition for fine-grained perception, and aggregation for robust prediction. First, we adopt the UVI maps, which densely build a bridge between 2D pixels and 3D vertexes, as an intermediate representation to facilitate the learning of image-to-model mapping. Second, we decompose the prediction task into one global stream and multiple local streams so that the network not only provides global perception for the camera and shape prediction, but also has detailed perception for part pose prediction. Lastly, we aggregate the message from local streams to enhance the robustness of part pose prediction, where a position-aided rotation feature refinement strategy is proposed to exploit the spatial relationship between body parts. Such a refinement strategy is more efficient since the correlations between position features are stronger than that in the original rotation feature space. The effectiveness of our method is validated on the Human3.6M and UP-3D datasets. Experimental results show that the proposed method significantly improves the reconstruction performance in comparison with previous state-of-the-art methods. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/HongwenZhang/DaNet-3DHumanReconstrution
从单眼图像重建三维人体形状和姿态是一项具有挑战性的工作,尽管最新的基于学习的方法已经取得了令人满意的结果。常见的失配是由于图像到模型空间的映射高度非线性和人体模型基于旋转的姿态表示容易导致关节位置的漂移。在这项工作中,我们提出了分解-聚合网络(DaNet)来解决这些问题。DaNet包括三种新的设计,即UVI引导学习、细粒度感知分解和鲁棒预测聚合。首先,我们采用UVI映射,它密集地在2D像素和3D顶点之间建立桥梁,作为中间表示,以方便学习图像到模型的映射。其次,我们将预测任务分解为一个全局流和多个局部流,使得网络不仅可以为摄像机提供全局感知和形状预测,还可以为部分姿态预测提供详细的感知。最后,我们将局部流中的信息进行聚合,以增强零件姿态预测的鲁棒性,并提出了一种利用人体部位间空间关系的位置辅助旋转特征细化策略。由于位置特征之间的相关性比原始旋转特征空间强,因此这种细化策略更有效。在Human3.6M和UP-3D数据集上验证了该方法的有效性。实验结果表明,与现有的重建方法相比,该方法显著提高了重建的性能。我们的代码可以在https://github.com/HongwenZhang/DaNet-3DHumanReconstrution找到

8. DeCaFA: Deep Convolutional Cascade for Face Alignment In The Wild
《DeCaFA:用于野外面部对齐的深卷积级联》
- ICCV 2019
- semanticscholar
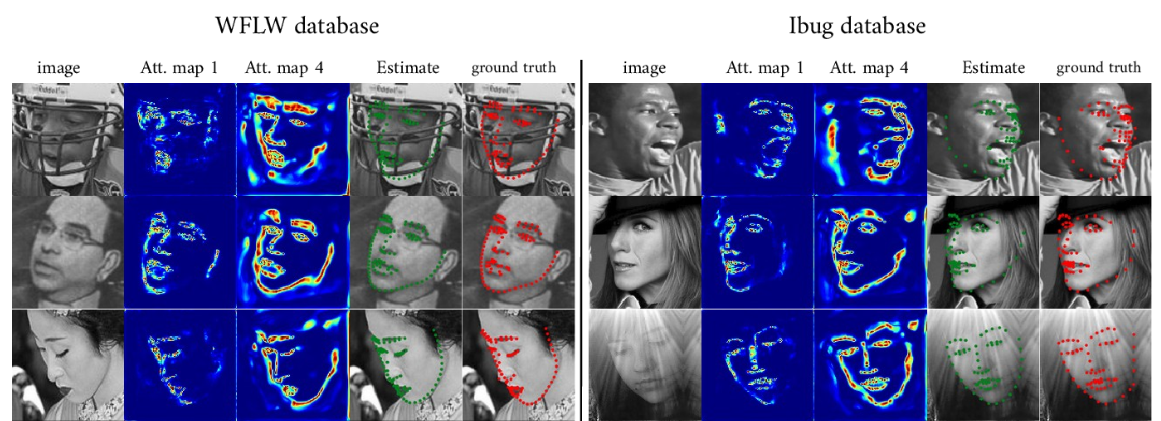
Face Alignment is an active computer vision domain, that consists in localizing a number of facial landmarks that vary across datasets. State-of-the-art face alignment methods either consist in end-to-end regression, or in refining the shape in a cascaded manner, starting from an initial guess. In this paper, we introduce DeCaFA, an end-to-end deep convolutional cascade architecture for face alignment. DeCaFA uses fully-convolutional stages to keep full spatial resolution throughout the cascade. Between each cascade stage, DeCaFA uses multiple chained transfer layers with spatial softmax to produce landmark-wise attention maps for each of several landmark alignment tasks. Weighted intermediate supervision, as well as efficient feature fusion between the stages allow to learn to progressively refine the attention maps in an end-to-end manner. We show experimentally that DeCaFA significantly outperforms existing approaches on 300W, CelebA and WFLW databases. In addition, we show that DeCaFA can learn fine alignment with reasonable accuracy from very few images using coarsely annotated data.
人脸定位是一个活跃的计算机视觉领域,它包括定位大量的不同数据集的面部地标。目前最先进的人脸定位方法要么是端到端回归,要么是从最初的猜测开始,以级联的方式细化形状。本文介绍了一种面向人脸对齐的端到端深卷积级联结构DeCaFA。DeCaFA使用全卷积级联来保持整个级联的空间分辨率。在每个级联阶段之间,DeCaFA使用带有空间softmax的多个链接传输层,为几个地标对齐任务中的每个任务生成陆标智能注意力地图。加权中间监督,以及各阶段之间的有效的特征融合,允许学习以端到端的方式逐步细化注意力地图。我们通过实验证明,DeCaFA在300W、CelebA和WFLW数据库上显著优于现有方法。此外,我们证明,DeCaFA可以使用粗略注释的数据,从很少的图像中获得合理的精度。

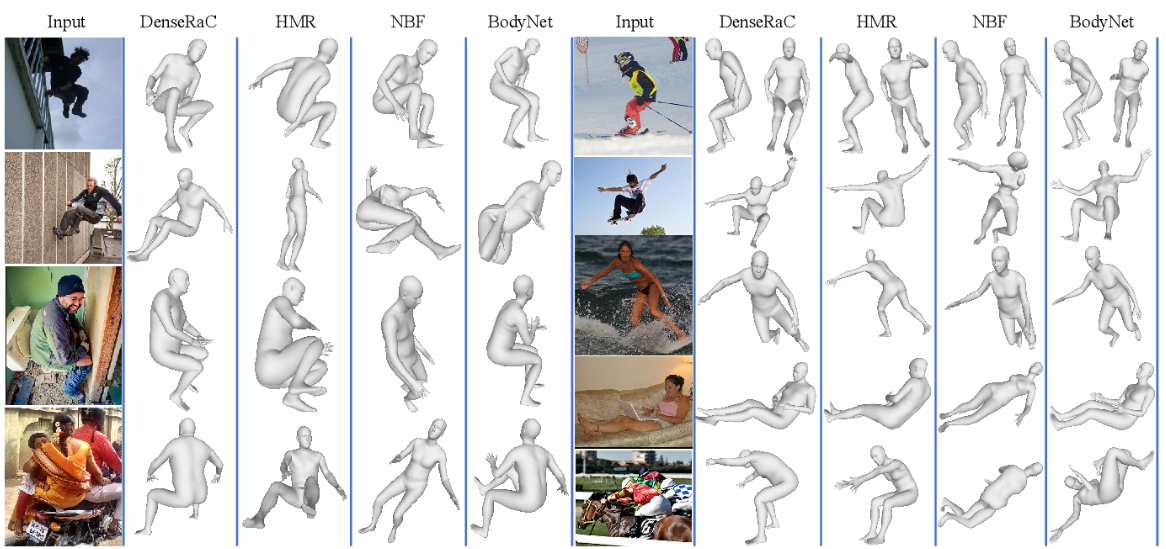
9. DenseRaC: Joint 3D Pose and Shape Estimation by Dense Render-and-Compare
《DenseRaC:通过密集渲染和比较,联合三维姿态和形状估计》
- 2019
We present DenseRaC, a novel end-to-end framework for jointly estimating 3D human pose and body shape from a monocular RGB image. Our two-step framework takes the body pixel-to-surface correspondence map (i.e., IUV map) as proxy representation and then performs estimation of parameterized human pose and shape. Specifically, given an estimated IUV map, we develop a deep neural network optimizing 3D body reconstruction losses and further integrating a render-and-compare scheme to minimize differences between the input and the rendered output, i.e., dense body landmarks, body part masks, and adversarial priors. To boost learning, we further construct a large-scale synthetic dataset (MOCA) utilizing web-crawled Mocap sequences, 3D scans and animations. The generated data covers diversified camera views, human actions and body shapes, and is paired with full ground truth. Our model jointly learns to represent the 3D human body from hybrid datasets, mitigating the problem of unpaired training data. Our experiments show that DenseRaC obtains superior performance against state of the art on public benchmarks of various humanrelated tasks.
我们提出了一种新的端到端框架DenseRaC,用于从单目RGB图像中联合估计三维人体姿态和体型。我们的两步框架采取身体像素到表面的对应映射(即。作为代理表示,然后对参数化的人体姿态和形状进行估计。具体来说,给定一个估计的IUV图,我们开发了一个深度神经网络优化三维人体重建损失,并进一步整合一个渲染和比较方案,以最小化输入和渲染输出之间的差异,即。密集的身体标志,身体部分的面具,和对抗性的先验。为了提高学习效率,我们进一步利用网络抓取的动作捕捉序列、3D扫描和动画构建了大规模的综合数据集(MOCA)。生成的数据涵盖了多样化的摄像机视角、人类动作和体型,并与完整的地面真相相匹配。我们的模型联合学习从混合数据集中表示三维人体,缓解了训练数据不配对的问题。我们的实验表明,DenseRaC在各种与人类相关的任务的公共基准测试中取得了优于现有水平的性能。
10. Dual Grid Net: hand mesh vertex regression from single depth maps
We present a method for recovering the dense 3D surface of the hand by regressing the vertex coordinates of a mesh model from a single depth map. To this end, we use a two-stage 2D fully convolutional network architecture. In the first stage, the network estimates a dense correspondence field for every pixel on the depth map or image grid to the mesh grid. In the second stage, we design a differentiable operator to map features learned from the previous stage and regress a 3D coordinate map on the mesh grid. Finally, we sample from the mesh grid to recover the mesh vertices, and fit it an articulated template mesh in closed form. During inference, the network can predict all the mesh vertices, transformation matrices for every joint and the joint coordinates in a single forward pass. When given supervision on the sparse key-point coordinates, our method achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on NYU dataset for key point localization while recovering mesh vertices and a dense correspondence map. Our framework can also be learned through self-supervision by minimizing a set of data fitting and kinematic prior terms. With multi-camera rig during training to resolve self-occlusion, it can perform competitively with strongly supervised methods Without any human annotation. LESS
提出了一种从单深度图回归网格模型顶点坐标来恢复手部密集三维曲面的方法。为此,我们使用了一个两阶段的2D全卷积网络架构。在第一个阶段,网络对深度图或图像网格上的每个像素估计一个密集的对应字段到网格。在第二阶段,我们设计了一个可微算子来映射前一阶段学习到的特征,并在网格上对三维坐标映射进行回归。最后,我们从网格中采样来恢复网格顶点,并以封闭的形式将其拟合为铰接模板网格。在推理过程中,该网络可以预测所有的网格顶点、每个节点的变换矩阵以及单个前向遍历的节点坐标。在稀疏关键点坐标的监督下,我们的方法在NYU数据集上达到了最先进的关键点定位精度,同时恢复网格顶点和稠密对应映射。我们的框架也可以通过最小化一组数据拟合和运动学先验项来通过自我监督来学习。在训练过程中使用多摄像机来解决自遮挡问题,它可以在没有任何人工标注的情况下,通过严格监督的方法进行竞争。
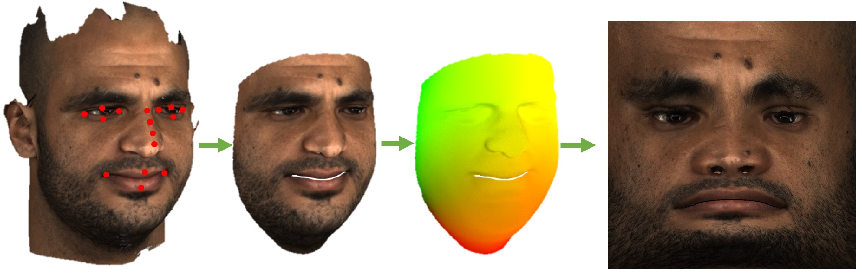
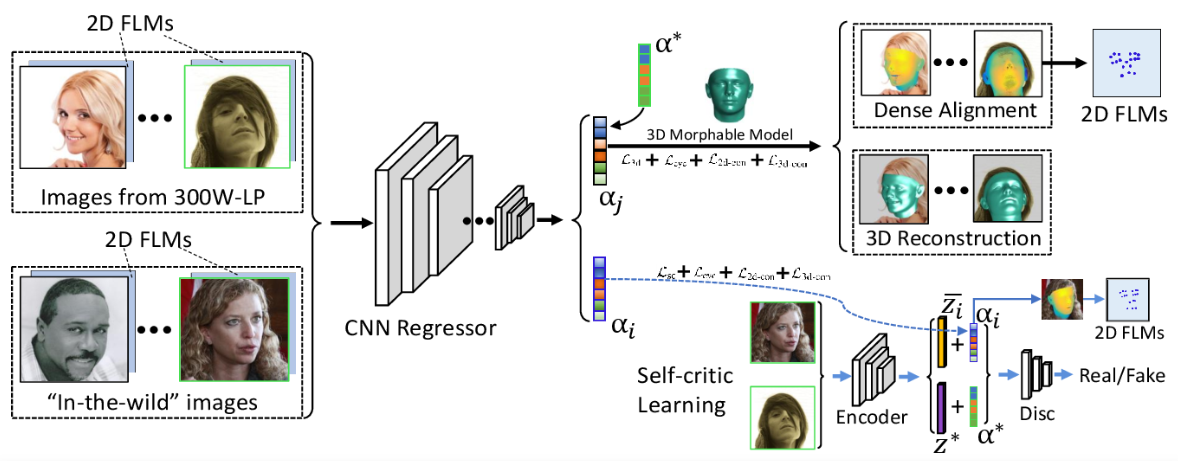
11. Joint 3D Face Reconstruction and Dense Face Alignment from A Single Image with 2D-Assisted Self-Supervised Learning
《利用二维辅助自监督学习技术,对单个图像进行联合三维人脸重建和密集人脸对齐》
3D face reconstruction from a single 2D image is a challenging problem with broad applications. Recent methods typically aim to learn a CNN-based 3D face model that regresses coefficients of 3D Morphable Model (3DMM) from 2D images to render 3D face reconstruction or dense face alignment. However, the shortage of training data with 3D annotations considerably limits performance of those methods. To alleviate this issue, we propose a novel 2D-assisted self-supervised learning (2DASL) method that can effectively use “in-the-wild” 2D face images with noisy landmark information to substantially improve 3D face model learning. Specifically, taking the sparse 2D facial landmarks as additional information, 2DSAL introduces four novel self-supervision schemes that view the 2D landmark and 3D landmark prediction as a self-mapping process, including the 2D and 3D landmark self-prediction consistency, cycle-consistency over the 2D landmark prediction and self-critic over the predicted 3DMM coefficients based on landmark predictions. Using these four self-supervision schemes, the 2DASL method significantly relieves demands on the the conventional paired 2D-to-3D annotations and gives much higher-quality 3D face models without requiring any additional 3D annotations. Experiments on multiple challenging datasets show that our method outperforms state-of-the-arts for both 3D face reconstruction and dense face alignment by a large margin.
单张二维图像的三维人脸重建是一个具有广泛应用前景的难题。目前的方法主要是学习一种基于cnn的三维人脸模型,该模型将三维可变形模型(3DMM)的系数从二维图像中回归,从而实现三维人脸重建或密集人脸对齐。然而,缺乏3D标注的训练数据在很大程度上限制了这些方法的性能。为了缓解这一问题,我们提出了一种新颖的2D-assisted self-supervised learning (2DASL)方法,该方法可以有效地利用具有噪声地标信息的“野外”2D人脸图像,大幅提高3D人脸模型的学习效果。特别,稀疏的2 d面部地标作为附加信息,2 dsal介绍四个小说自身的监督计划这一观点2 d地标和3 d具有里程碑意义的预测self-mapping过程,包括2 d和3 d地标self-prediction一致性,在2 d cycle-consistency具有里程碑意义的预测和令人欣喜的预测3 dmm系数基于里程碑式的预测。通过这四种自我监督方案,2DASL方法大大降低了传统的2d -3D配对注释的要求,在不需要额外3D注释的情况下,提供了更高质量的3D人脸模型。在多个具有挑战性的数据集上进行的实验表明,我们的方法在三维人脸重建和密集人脸对齐方面都有较大的优势。
12. HoloPose : Real Time Holistic 3 D Human Reconstruction InThe-Wild
《全息:野外实时整体三维人体重建》
2019
使用DensePose搭建的实施转换系统
Figure 1: We introduce HoloPose, a method for holistic monocular 3D body reconstruction in-the-wild. We start with an accurate, part-based estimate of 3D model parameters θ, and decoupled, FCN-based estimates of DensePose, 2D and 3D joints. We then efficiently optimize a misalignment loss Ltotal(θ) between the top-down 3D model predictions to the bottomup pose estimates, thereby largely improving alignment. The 3D model estimation and iterative fitting steps are efficiently implemented as network layers, facilitating multi-person 3D pose estimation in-the-wild at more than 10 frames per second
图1:我们介绍了HoloPose,一种在野外进行整体单眼三维身体重建的方法。我们从一个精确的开始,部分原因估计的3 d模型参数θ,解耦,FCN-based DensePose估计,2 d和3 d关节。然后我们有效地优化偏差损失Ltotal(θ)之间的自顶向下的3 d模型预测bottomup姿势估计,从而很大程度上提高对齐。将三维模型估计和迭代拟合步骤有效地实现为网络层,以超过每秒10帧的速度实现多人三维姿态估计
13. A Neural Network for Detailed Human Depth Estimation from a Single Image
- 2019
《一种用于从单个图像中详细估计人体深度的神经网络》
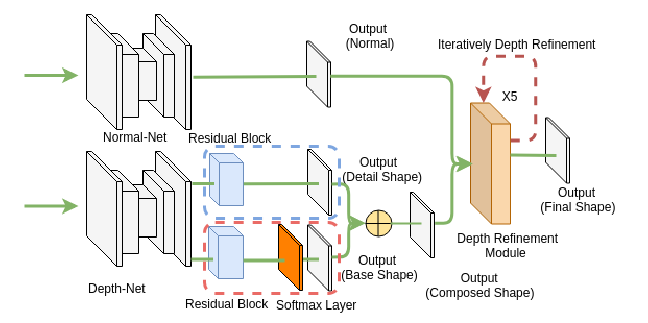
This paper presents a neural network to estimate a detailed depth map of the foreground human in a single RGB image. The result captures geometry details such as cloth wrinkles, which are important in visualization applications. To achieve this goal, we separate the depth map into a smooth base shape and a residual detail shape and design a network with two branches to regress them respectively. We design a training strategy to ensure both base and detail shapes can be faithfully learned by the corresponding network branches. Furthermore, we introduce a novel network layer to fuse a rough depth map and surface normals to further improve the final result. Quantitative comparison with fused `ground truth’ captured by real depth cameras and qualitative examples on unconstrained Internet images demonstrate the strength of the proposed method
提出了一种基于神经网络的单RGB图像前景人物深度细节估计方法。结果捕获了诸如织物褶皱等几何细节,这些在可视化应用中非常重要。为了实现这一目标,我们将深度图分为平滑的基础形状和剩余的细节形状,并设计了一个具有两个分支的网络分别对它们进行回归。我们设计了一个训练策略,以确保基础形状和细节形状都能被相应的网络分支忠实地学习。在此基础上,我们引入了一种新的网络层来融合粗糙深度图和表面法线以进一步提高最终结果。通过与真实深度相机捕获的融合“地面真实”的定量比较和对无约束网络图像的定性分析,验证了该方法的有效性
Other:
A Review of Facial Landmark Extraction in 2D Images and Videos Using Deep Learning
用深度学习技术提取二维图像和视频中的面部特征的研究进展
Dense Cloth (FashionAI)
- Dense Cloth 换装;
- Dense Pose-guild Image 生成,
1. 360-Degree Textures of People in Clothing from a Single Image
《人的衣服360度纹理–从单一的形象》
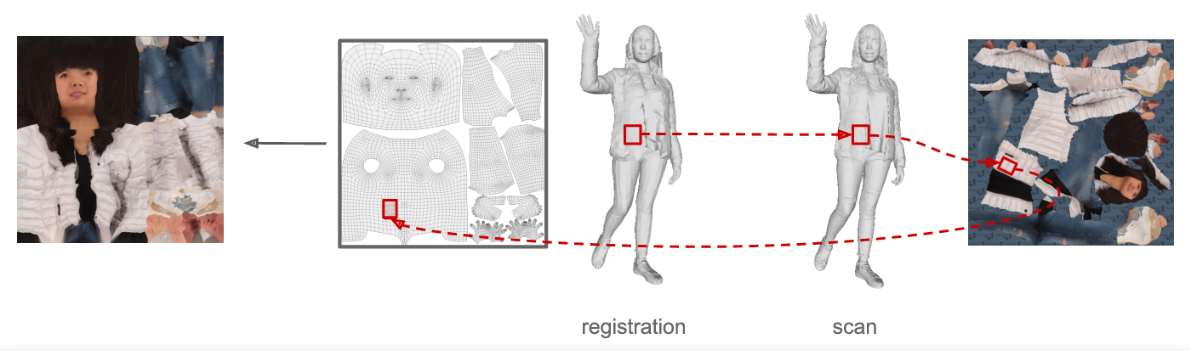
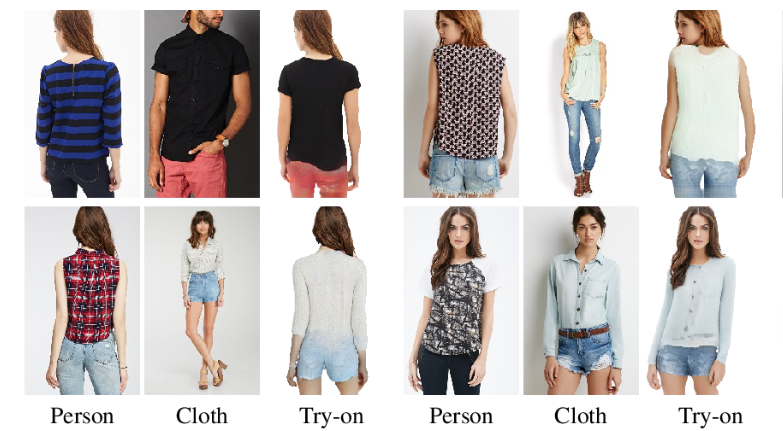
In this paper we predict a full 3D avatar of a person from a single image. We infer texture and geometry in the UV-space of the SMPL model using an image-to-image translation method. Given partial texture and segmentation layout maps derived from the input view, our model predicts the complete segmentation map, the complete texture map, and a displacement map. The predicted maps can be applied to the SMPL model in order to naturally generalize to novel poses, shapes, and even new clothing. In order to learn our model in a common UV-space, we non-rigidly register the SMPL model to thousands of 3D scans, effectively encoding textures and geometries as images in correspondence. This turns a difficult 3D inference task into a simpler image-to-image translation one. Results on rendered scans of people and images from the DeepFashion dataset demonstrate that our method can reconstruct plausible 3D avatars from a single image. We further use our model to digitally change pose, shape, swap garments between people and edit clothing. To encourage research in this direction we will make the source code available for research purpose [5]
在这篇论文中,我们预测一个人的完整的3D头像从一个单一的图像。我们使用图像到图像的转换方法在SMPL模型的uv空间中推断出纹理和几何形状。根据输入视图中的局部纹理和分割布局图,我们的模型可以预测完整的分割图、完整的纹理图和位移图。预测的地图可以应用于SMPL模型,以便自然地推广到新的姿势、形状,甚至新衣服。为了在公共uv空间中学习我们的模型,我们不严格地将SMPL模型注册到数千次3D扫描中,有效地将纹理和几何图形编码为对应的图像。这将一个困难的3D推理任务变成了一个更简单的图像到图像的转换任务。对DeepFashion数据集中的人物和图像的渲染扫描结果表明,我们的方法可以从一张图像重建可信的3D头像。我们进一步使用我们的模型来数字化地改变姿势、形状、在人们之间交换衣服和编辑衣服。为了鼓励这方面的研究,我们将把源代码提供给研究目的[5]
2. DwNet: Dense warp-based network for pose-guided human video generation
《DwNet:密集的基于翘曲的网络,用于位置引导的人类视频生成》
- 2019
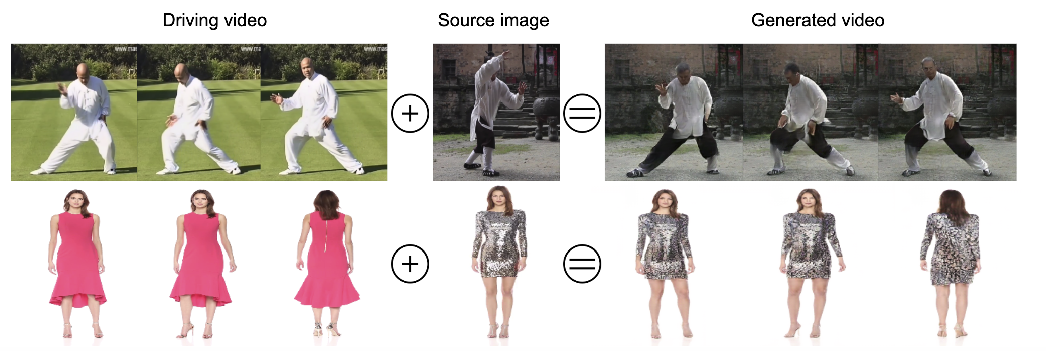
Generation of realistic high-resolution videos of human subjects is a challenging and important task in computer vision. In this paper, we focus on human motion transfer - generation of a video depicting a particular subject, observed in a single image, performing a series of motions exemplified by an auxiliary (driving) video. Our GAN-based architecture, DwNet, leverages dense intermediate pose-guided representation and refinement process to warp the required subject appearance, in the form of the texture, from a source image into a desired pose. Temporal consistency is maintained by further conditioning the decoding process within a GAN on the previously generated frame. In this way a video is generated in an iterative and recurrent fashion. We illustrate the efficacy of our approach by showing state-of-the-art quantitative and qualitative performance on two benchmark datasets: TaiChi and Fashion Modeling. The latter is collected by us and will be made publicly available to the community.
生成逼真的高分辨率人体视频是计算机视觉领域的一项重要任务。在这篇论文中,我们关注的是人体运动的转移——以一个辅助(驱动)视频为例,在一个单独的图像中观察一个特定对象的视频,并执行一系列的运动。我们基于gan的架构DwNet利用密集的中间位置引导表示和细化过程,以纹理的形式将所需的主题外观从源图像扭曲为所需的姿态。时间一致性是通过进一步调整GAN中先前生成的帧上的解码过程来保持的。通过这种方式,视频以迭代和重复的方式生成。我们通过在太极和时尚建模两个基准数据集上展示最先进的定量和定性性能来说明我们的方法的有效性。后者由我们收集,并将向社会公开。
对原图的换衣效果还行,转Pose效果较差
3. Coordinate-based Texture Inpainting for Pose-Guided Image Generation
- 2018
- pose-guided resynthesis of human photographs
- coordinate-base 基于坐标的纹理修复
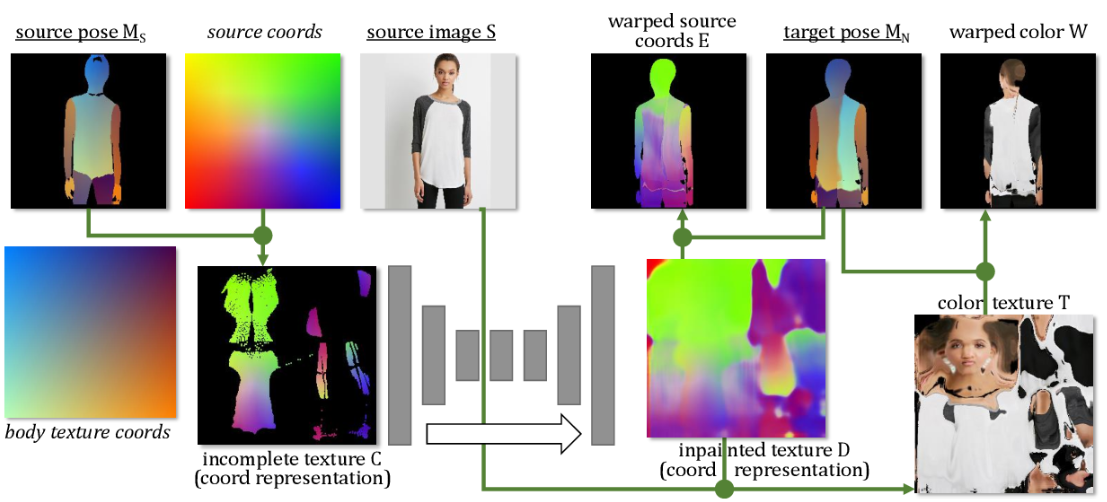
We present a new deep learning approach to pose-guided resynthesis of human photographs. At the heart of the new approach is the estimation of the complete body surface texture based on a single photograph. Since the input photograph always observes only a part of the surface, we suggest a new inpainting method that completes the texture of the human body. Rather than working directly with colors of texture elements, the inpainting network estimates an appropriate source location in the input image for each element of the body surface. This correspondence field between the input image and the texture is then further warped into the target image coordinate frame based on the desired pose, effectively establishing the correspondence between the source and the target view even when the pose change is drastic. The final convolutional network then uses the established correspondence and all other available information to synthesize the output image. A fully-convolutional architecture with deformable skip connections guided by the estimated correspondence field is used. We show state-of-the-art result for pose-guided image synthesis. Additionally, we demonstrate the performance of our system for garment transfer and pose-guided face resynthesis.
我们提出了一种新的深度学习方法,以位置引导重新合成人体照片。新方法的核心是基于一张照片来估计整个身体表面的纹理。由于输入的照片总是只观察到表面的一部分,我们提出了一种新的绘画方法来完成人体的纹理。与直接处理纹理元素的颜色不同,inpainting网络在输入图像中为身体表面的每个元素估计一个合适的源位置。然后,将输入图像与纹理之间的对应字段根据所需的位姿进一步扭曲到目标图像坐标系中,从而在位姿变化剧烈的情况下有效地建立源和目标视图之间的对应关系。最后的卷积网络使用建立的通信和所有其他可用信息来合成输出图像。采用全卷积结构,在估计对应域的引导下实现可变形的跳跃连接。我们展示了位置引导图像合成的最新成果。此外,我们还演示了我们的系统在服装转移和位置导向面部合成方面的性能

4. MoCoGAN: Decomposing Motion and Content for Video Generation
《MoCoGAN:分解运动和内容,生成视频》
https://github.com/sergeytulyakov/mocogan
Visual signals in a video can be divided into content and motion. While content specifies which objects are in the video, motion describes their dynamics. Based on this prior, we propose the Motion and Content decomposed Generative Adversarial Network (MoCoGAN) framework for video generation. The proposed framework generates a video by mapping a sequence of random vectors to a sequence of video frames. Each random vector consists of a content part and a motion part. While the content part is kept fixed, the motion part is realized as a stochastic process. To learn motion and content decomposition in an unsupervised manner, we introduce a novel adversarial learning scheme utilizing both image and video discriminators. Extensive experimental results on several challenging datasets with qualitative and quantitative comparison to the state-of-theart approaches, verify effectiveness of the proposed framework. In addition, we show that MoCoGAN allows one to generate videos with same content but different motion as well as videos with different content and same motion.
视频中的视觉信号可以分为内容和动作。内容指定了视频中的对象,而动作描述了它们的动态。在此基础上,提出了视频生成的运动和内容分解生成对抗网络(MoCoGAN)框架。该框架通过将随机向量序列映射到视频帧序列来生成视频。每个随机向量由一个内容部分和一个运动部分组成。在内容部分保持不变的情况下,运动部分实现为随机过程。为了以无监督的方式学习运动和内容分解,我们引入了一种利用图像和视频鉴别器的对抗学习方案。在几个具有挑战性的数据集上的大量实验结果,定性和定量地与最先进的方法进行比较,验证了所提框架的有效性。此外,我们还演示了MoCoGAN可以生成内容相同但动作A Neural Network for Detailed Human Depth Estimation from a Single Image不同的视频,以及内容不同但动作相同的视频。
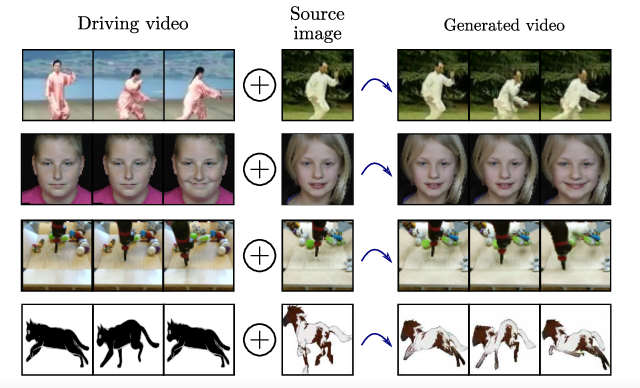
5. Animating Arbitrary Objects via Deep Motion Transfer
《通过深动作传输来制作任意物体的动画》
- 对象+动作序列 — > 动画
- https://github.com/AliaksandrSiarohin/monkey-net
This paper introduces a novel deep learning framework for image animation. Given an input image with a target object and a driving video sequence depicting a moving object, our framework generates a video in which the target object is animated according to the driving sequence. This is achieved through a deep architecture that decouples appearance and motion information. Our framework consists of three main modules: (i) a Keypoint Detector unsupervisely trained to extract object keypoints, (ii) a Dense Motion prediction network for generating dense heatmaps from sparse keypoints, in order to better encode motion information and (iii) a Motion Transfer Network, which uses the motion heatmaps and appearance information extracted from the input image to synthesize the output frames. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on several benchmark datasets, spanning a wide variety of object appearances, and show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art image animation and video generation methods. Our source code is publicly available.
提出了一种新的图像动画深度学习框架。给定目标对象的输入图像和描述运动对象的驱动视频序列,我们的框架生成一个视频,其中目标对象根据驱动序列进行动画。这是通过一个深入的架构来实现的,它将外观和动作信息解耦。我们的框架包括三个主要模块:(i)关键点检测器unsupervisely训练要点提取对象,(2)一个密集的运动预测网络从稀疏生成致密的热图要点、为了更好的编码运动信息和(iii)运动传输网络,它使用运动的热图和外观信息从输入图像中提取合成输出帧。我们证明了我们的方法在几个基准数据集的有效性,跨越了广泛的对象外观,并表明我们的方法优于最先进的图像动画和视频生成方法。我们的源代码是公开的。
6. Convolutional Mesh Regression for Single-Image Human Shape Reconstruction
《卷积网格回归用于单图像人体形态重建》
- 单目图像三维人体重建
https://github.com/nkolot/GraphCMR
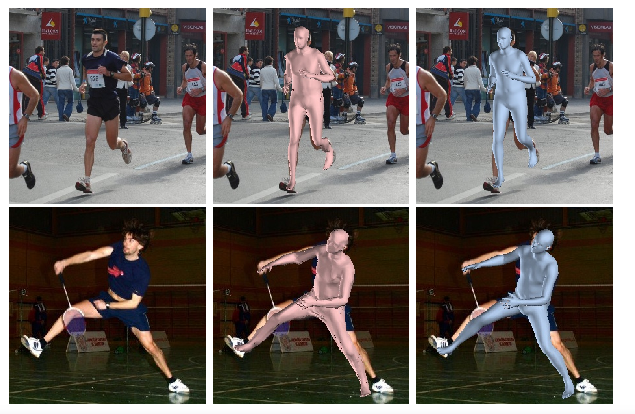
This paper addresses the problem of 3D human pose and shape estimation from a single image. Previous approaches consider a parametric model of the human body, SMPL, and attempt to regress the model parameters that give rise to a mesh consistent with image evidence. This parameter regression has been a very challenging task, with model-based approaches underperforming compared to nonparametric solutions in terms of pose estimation. In our work, we propose to relax this heavy reliance on the model’s parameter space. We still retain the topology of the SMPL template mesh, but instead of predicting model parameters, we directly regress the 3D location of the mesh vertices. This is a heavy task for a typical network, but our key insight is that the regression becomes significantly easier using a Graph-CNN. This architecture allows us to explicitly encode the template mesh structure within the network and leverage the spatial locality the mesh has to offer. Image-based features are attached to the mesh vertices and the Graph-CNN is responsible to process them on the mesh structure, while the regression target for each vertex is its 3D location. Having recovered the complete 3D geometry of the mesh, if we still require a specific model parametrization, this can be reliably regressed from the vertices locations. We demonstrate the flexibility and the effectiveness of our proposed graph-based mesh regression by attaching different types of features on the mesh vertices. In all cases, we outperform the comparable baselines relying on model parameter regression, while we also achieve state-of-the-art results among model-based pose estimation approaches

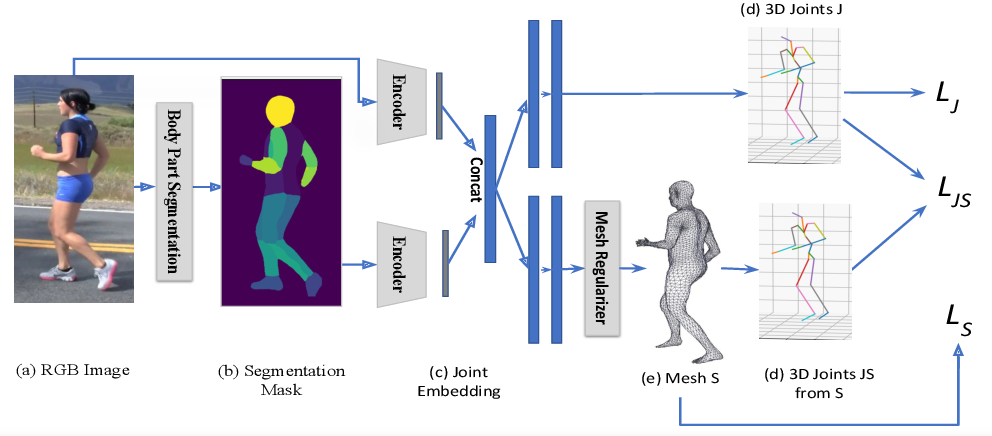
7. HumanMeshNet: Polygonal Mesh Recovery of Humans
《HumanMeshNet:多边形网格恢复人类》
- 单目图像三维人体重建
https://github.com/yudhik11/HumanMeshNet
3D Human Body Reconstruction from a monocular image is an important problem in computer vision with applications in virtual and augmented reality platforms, animation industry, en-commerce domain, etc. While several of the existing works formulate it as a volumetric or parametric learning with complex and indirect reliance on re-projections of the mesh, we would like to focus on implicitly learning the mesh representation. To that end, we propose a novel model, HumanMeshNet, that regresses a template mesh’s vertices, as well as receives a regularization by the 3D skeletal locations in a multi-branch, multi-task setup. The image to mesh vertex regression is further regularized by the neighborhood constraint imposed by mesh topology ensuring smooth surface reconstruction. The proposed paradigm can theoretically learn local surface deformations induced by body shape variations and can therefore learn high-resolution meshes going ahead. We show comparable performance with SoA (in terms of surface and joint error) with far lesser computational complexity, modeling cost and therefore real-time reconstructions on three publicly available datasets. We also show the generalizability of the proposed paradigm for a similar task of predicting hand mesh models. Given these initial results, we would like to exploit the mesh topology in an explicit manner going ahead.
单目图像三维人体重建是计算机视觉领域的一个重要研究课题,在虚拟增强现实平台、动漫产业、电子商务等领域有着广泛的应用。虽然现有的一些作品将其描述为一种复杂且间接地依赖于网格重投影的体积或参数学习,但我们希望将重点放在对网格表示的隐式学习上。为此,我们提出了一个新的模型,HumanMeshNet,该模型对模板网格的顶点进行回归,并通过多分支、多任务设置中的3D骨骼位置进行正则化。利用网格拓扑所施加的邻域约束进一步正则化网格顶点回归图像,保证了曲面重建的平稳性。提出的模型在理论上可以学习由体型变化引起的局部表面变形,因此可以学习未来的高分辨率网格。我们展示了与SoA相当的性能(在表面和联合错误方面),并且计算复杂度、建模成本和因此在三个公开数据集上的实时重构都要低得多。我们还展示了所提出的范例的通用性,为类似的任务预测手网格模型。考虑到这些初始结果,我们希望以一种显式的方式利用网格拓扑。
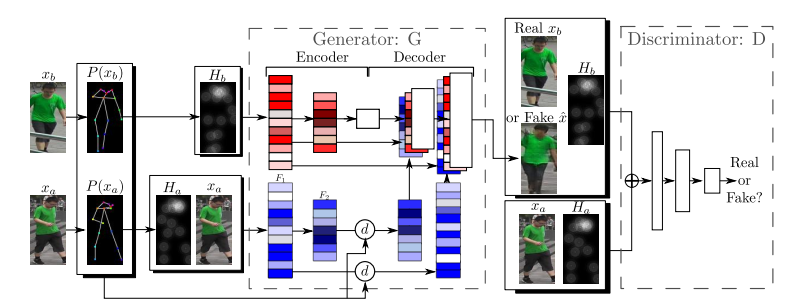
8. [Deformable GANs] for Pose-based Human Image Generation
- Deformable GANs
In this paper we address the problem of generating person images conditioned on a given pose. Specifically, given an image of a person and a target pose, we synthesize a new image of that person in the novel pose. In order to deal with pixel-to-pixel misalignments caused by the pose differences, we introduce deformable skip connections in the generator of our Generative Adversarial Network. Moreover, a nearest-neighbour loss is proposed instead of the common L1 and L2 losses in order to match the details of the generated image with the target image. We test our approach using photos of persons in different poses and we compare our method with previous work in this area showing state-of-the-art results in two benchmarks. Our method can be applied to the wider field of deformable object generation, provided that the pose of the articulated object can be extracted using a keypoint detector
在这篇论文中,我们讨论了在给定姿态条件下生成人物图像的问题。具体来说,给定一个人的图像和一个目标姿势,我们合成一个新的人的图像在新的姿势。为了解决由位姿差异引起的像素间的不匹配问题,我们在生成对抗网络的生成器中引入了可变形的跳跃连接。此外,为了使生成的图像与目标图像的细节匹配,我们提出了一种最近邻损失来代替常见的L1和L2损失。我们使用不同姿势的人的照片来测试我们的方法,并将我们的方法与之前在这一领域的工作进行比较,在两个基准中显示出最先进的结果。我们的方法可以应用于更广泛的可变形对象生成领域,前提是可以使用关键点检测器提取关节对象的位姿
GM
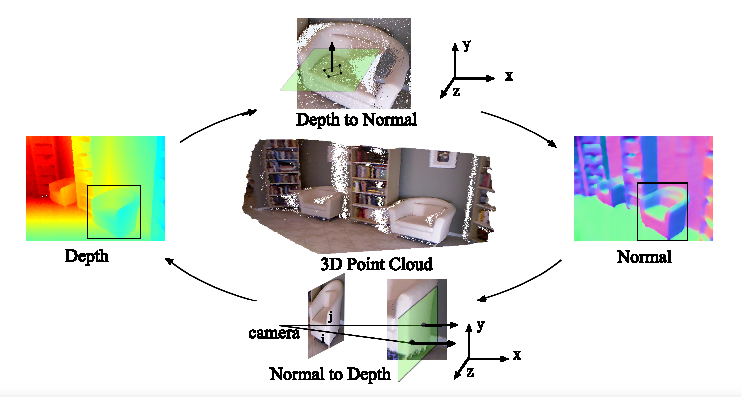
GeoNet: Geometric Neural Network for Joint Depth and Surface Normal Estimation