[TOC]
相关书籍
入门
C++ Primer Plus
C++ Primer
提高
深度探索C++对象模型
More Effective C++ 35
Effective C++ 55
Effective Modern C++
进阶篇
STL 源码剖析
C++标准库
GOF23 设计模式 C++
C++并发编程实战
C++性能优化指南
网络编程
Linux多线程-服务端编程-
Unix网络编程 三件套
TCP/UP协议 三卷
APIs 标准库 1.int/float to string/array: C语言提供了几个标准库函数,可以将任意类型(整型、长整型、浮点型等)的数字转换为字符串,下面列举了各函数的方法及其说明。
除此外,还可以使用sprintf 系列函数把数字转换成字符串,其比itoa()系列函数运行速度慢
2. string/array to int/float C/C++语言提供了几个标准库函数,可以将字符串转换为任意类型(整型、长整型、浮点型等)。
● atof():将字符串转换为双精度浮点型值。
数据类型&变量&常量 int to string 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 int a = 10 ;char *intStr = itoa (a);string str = string (intStr); stringstream ss; ss << a; string str = ss.str (); #include <string> std::string s = std::to_string (42 ); #include <sstream> #define SSTR(x) static_cost<std::ostringstream &> ((std::ostringstream() << std::dec << x)).str() #include <boost/lexical_cast.hpp> int num = 4 ;std::string str = boost::lexical_cast <std::string>(num);
rand 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 #include <stdlib.h> int N = rand () % 11 ; int N = rand () % 10 ; int N = 1 + rand () % 10 ; a + rand () % n if (1 ==rand()%10 ) else
修饰符 unsinge
存储类
auto
register
static 全局变量
extern 全局变量的引用
mutable
thread_local (C++11)
const (只读变量)
constptr (常量)
从 C++ 17 开始,auto 关键字不再是 C++ 存储类说明符,且 register 关键字被弃用。
运算符 循环 判断 函数 1 2 3 void func (Cobject* object) void func (Cobect& object) void func (Cobject object)
有什么区别呢?
void func(Cobject* object)
这种方式是将类指针 作为参数,函数压入参数时实际上复制了指针的值(其实指针可以看作一个存放地址值的×××),实际复制的指针仍指向原对象的空间 ,所以func函数对该指针的操作是对原对象空间的操作。
void func(Cobject& object)
这种方式和传指针类似,但函数压入参数时实际上复制了object对象的this指针,其实this指针不是一个真正存在的指针,可以看作是每个对象的数据空间起始地址。func函数中对this指针的操作,实际上也是对原对象空间的操作 。
void func(Cobject object)
这种函数是非常不建议的,因为函数参数压栈时,对object进行了复制(还记得拷贝构造函数吗),所以函数对object的操作实际上是对新的对象空间进行的操作,不会影响原对象空间。由于不必要的拷贝对象是十分浪费时间的,也没有意义,我们完全可以用下面函数代替
1 func (const Cobject& object)
这样也能保护对象的只读性质。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1 、值传递 实参是变量,表达式等值。 find(int x){} y= find (z); 上面的例子中,z是实参,x是形参。x变z不变。 在值传递过程中,实参和形参位于内存中两个不同地址中,实参先自己复制一次拷贝,再把拷贝复制给形参。所以,在值传递过程中,形参的变化不会对实参有任何的影响。 2 、地址传递(也称引用传递) 实参是指针。 在函数调用的时候,实参传递给你的是指针地址,地址一样也就意味着实参和形参是一样的,当你的形参发生改变时,实参也会发生改变。 find(int &x){} y= find (z); 上面的例子中,z是实参,x是形参。z随x而改变。
数字运算 cos, sin tan, log, pow,
hypot, sqrt, abs, fabs, floor
数组 [C++]指针数组以及数组初始化
枚举enum 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 enum < enum color_set1 { enum week { 各枚举常量的值可以重复。例如: enum fruit_set {1 , peach, grape} enum week {Sun=7 , Mon=1 , Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat}; 枚举常量只能以标识符形式表示,而不能是整型、字符型等文字常量。例如,以下定义非法: enum letter_set {'a' ,'d' ,'F' ,'s' ,'T' }; enum year_set {2000 ,2001 ,2002 ,2003 ,2004 ,2005 }; 可改为以下形式则定义合法: enum letter_set { enum year_set {
字符串String 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 ## string -> char* #### data()方法,如: 1 string str = "hello" ;2 const char * p = str.data();#### c_str()方法,如: 1 string str=“world”;2 const char *p = str.c_str();#### copy()方法,如: 1 string str="hmmm" ;2 char p[50 ];3 str.copy(p, 5 , 0 );4 *(p+5 )=‘\0 ’;## 二、char * -> string #### 1 string s;2 char *p = "hello" ;3 s = p; ## 三、string 转char [] 1 string pp = "dagah" ;2 char p[8 ];3 int i;4 for ( i=0 ;i<pp.length();i++)5 p[i] = pp[i];6 p[i] = '\0' ;7 printf ("%s\n" ,p);8 cout <<p;
string 赋值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 #include <sstream> ostringstream buffer; buffer << "sss," << 2015 << "_" << 1 ; string str = buffer.str (); char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];sprintf (buffer,"%s_%d_%d" ,"cplusplus" ,2015 ,1 );string str = buffer;
string.substr(起点, length) 1 2 operate_str = initial_str.substr(0 , 3 );
string.erase() 1 2 3 4 5 6 1.erase(pos,n); 删除从下标pos开始的n个字符,比如erase(0,1)就是删除第一个字符 2.erase(position); 删除postion处的一个字符(position是一个string类型的迭代器) 3.erase(first,last) 删除从first到last之间的字符(first和last都是迭代器)
string 对比 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 std ::string h2 = "BUS_0001" ;std ::string h3 = "BUS_0001" ;printf (" h3 == h2: %d\n" ,h3 == h2);if (h3 == h2) h3.compare(h2) == 0
string 高级 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 string orderstr = "hello world" ; cout << "正序字符串:" << orderstr << endl; reverse(orderstr .begin(), orderstr.end());cout << "逆序字符串:" << orderstr << endl; ## 2.将一个字符串按照空格划分成单词 string str = "hello world, how are you?"; stringstream ss(str); string word; while (ss >> word) { cout << word << endl; }
指针 引用 memcpy…apis memset(void *str, int c, size_t n)
复制字符 c(一个无符号字符)到参数 str 所指向的字符串的前 n 个字符。
memcpy(void *destin, void *source, unsigned n);
从存储区 source复制n 个字节到存储区 destin。
将地址从src开始的前count个字节的内容拷贝到地址从dst开始的内存空间中。
文件读取I/O C++文件读写详解(ofstream,ifstream,fstream)
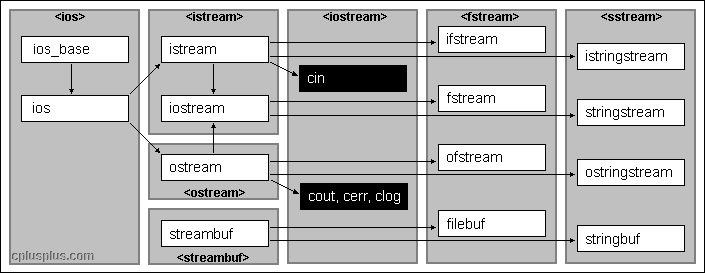
1、基于控制台io 1 2 3 4 #include <iostream> istream // 流读取 (input) ostream // 写入流 (output) iostram // 对流读写
2、基于文件IO [ifstream/ofstream] 1 2 3 4 5 6 #include <fstream> ifstream ofstream fstream
ref:
https://www.toptip.ca/2012/11/is-it-necessary-to-manually-close.html
3、基于字符串IO [i/ostringstream] 1 2 3 4 #include <sstream> istringstream ostringstream stringstream
ref:
c++的输入输出 [一](istream,ostream,iostream)
c++的输入输出 [二](ifstream,ofstream,fstream)
c++的输入输出 [三](istringstream,ostringstream,stringstream)
C++文件读写详解(ofstream,ifstream,fstream)
c++多进程读取同一个文件
C Plus 第 6.1 节 带文件的输入/输出
c++多线程:互斥锁
c++输入文件流ifstream用法详解_陈 洪 伟的博客-CSDN博客_ifstream用法
时间 1、时间戳毫秒/秒 gettimeofday() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <unistd.h> int main (int argc, char *argv[]) { struct timeval time ; gettimeofday(&time, NULL ); struct timeval time_now { gettimeofday(&time_now, nullptr); time_t msecs_time = (time_now.tv_sec * 1000 ) + (time_now.tv_usec / 1000 ); cout << "seconds since epoch( s): " << time_now.tv_sec << endl ; cout << "milliseconds since epoch(ms): " << msecs_time << endl << endl ; }
chrono 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <chrono> #include <iostream> #include <sys/time.h> #include <ctime> using std ::cout ; using std ::endl ; using std ::chrono::duration_cast; using std ::chrono::milliseconds; using std ::chrono::seconds; using std ::chrono::system_clock; int main () { auto millisec_since_epoch = duration_cast<milliseconds>(system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count(); auto sec_since_epoch = duration_cast<seconds>(system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count(); cout << "seconds since epoch: " << sec_since_epoch << endl ; cout << "milliseconds since epoch: " << millisec_since_epoch << endl ; auto tp = std ::chrono::system_clock::now(); auto seconds = std ::chrono::duration_cast<std ::chrono::seconds>(tp.time_since_epoch()); cout << seconds.count() << " s" << endl ; return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Demo
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 #include <cstdint> #include <ctime> #include <iostream> #include <chrono> #include <sstream> #include <iomanip> using namespace std ; void time_point_to_duration () ;void duration_to_time_point () ;void format_time_point () ;void parse_from_string () ;int main (int argc, char *argv[]) { time_point_to_duration(); duration_to_time_point(); format_time_point(); parse_from_string(); return 0 ; } void time_point_to_duration () { auto tp=std ::chrono::system_clock::now(); auto seconds=std ::chrono::duration_cast<std ::chrono::seconds>(tp.time_since_epoch()); cout <<seconds.count()<<" s" <<endl ; auto ms=std ::chrono::duration_cast<std ::chrono::milliseconds>(tp.time_since_epoch()); cout <<ms.count()<<" ms" <<endl ; auto us=std ::chrono::duration_cast<std ::chrono::microseconds>(tp.time_since_epoch()); cout <<us.count()<<" us" <<endl ; auto ns=std ::chrono::duration_cast<std ::chrono::nanoseconds>(tp.time_since_epoch()); cout <<ns.count()<<" ns" <<endl ; cout <<tp.time_since_epoch().count()<<" default is ns" <<endl ; } void duration_to_time_point () { std ::uint64_t ticker=1609756793160376465 ; auto ns=std ::chrono::nanoseconds(ticker); auto tp1=std ::chrono::time_point<std ::chrono::system_clock,std ::chrono::nanoseconds>(ns); auto tp2=tp1-std ::chrono::hours(1 ); cout <<"tp1=" <<tp1.time_since_epoch().count()<<endl <<"tp2=" <<tp2.time_since_epoch().count()<<endl ; } void format_time_point () { auto tp=std ::chrono::system_clock::now(); auto time=std ::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t (tp); std ::stringstream ss; ss<<std ::put_time(std ::localtime(&time),"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" ); cout <<ss.str()<<endl ; } void parse_from_string () { std ::stringstream ss; ss<<"2021-01-06 18:47:35" ; std ::tm tm{}; ss>>std ::get_time(&tm,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" ); auto tp=std ::chrono::system_clock::from_time_t (std ::mktime(&tm)); cout <<tp.time_since_epoch().count()<<endl ; }
掩耳盗铃 1 2 3 4 5 time_t now = time(nullptr);time_t mnow = now * 1000 ;cout << "seconds since epoch: " << now << endl ;cout << "milliseconds since epoch: " << mnow << endl << endl ;
Windows/Linux Get Millisecond
get time in millisecond
2、时间戳(s) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 time_t now = time(0 );tm *ltm = localtime(&now); char s[100 ]{};strftime(s, sizeof (s), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" , ltm); string timestr (s) ;
1 2 3 4 std ::time_t t = std ::time(NULL );std ::tm tm = *std ::localtime(&t);std ::cout .imbue(std ::locale("CHS" ));std ::cout << std ::put_time(&tm,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" ) << '\n' ;
3、localtime(time_t) C 库函数 struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timer) 使用 timer 的值来填充 tm 结构。timer 的值被分解为 tm 结构,并用本地时区表示。
4、strftime() size_t strftime(char *str, size_t count, const char *format, const struct tm *tm);
1 2 3 4 str, 表示返回的时间字符串 count, 要写入的字节的最大数量 format, 格式字符串由零个或多个转换符和普通字符(除%) tm, 输入时间
基本的输入输出 数据结构 APIs C++ 11 auto C++11这次的更新带来了令很多C++程序员期待已久的for range循环,每次看到javascript, lua里的for range,心想要是C++能有多好,心里别提多酸了。这次C++11不负众望,再也不用羡慕别家人的for range了。
字符串 & 数组
1 2 3 4 std::string str = “hello, world”; for (auto ch : str) { std::cout << ch << std::endl; }
1 2 3 4 int arr[] = {1 , 2 , 3 , 4 }; for (auto i : arr) { std::cout<< i << std::endl; }
stl 容器
1 2 3 4 std::vector<std::string> str_vec = {“i”, “like”, "google”}; for(auto& it : str_vec) { it = “c++”; }
遍历stl map
1 2 3 4 std::map<int , std::string> hash_map = {{1 , “c++”}, {2 , “java”}, {3 , “python”}}; for (auto it : hash_map) { std::cout << it.first << “\t” << it.second << std::endl; }
算法 迭代器 对象 对象创建 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Person p1; cout <<endl ;Person p2 (18 , "lili" ) ; cout <<endl ;Person p3 = Person(); cout <<endl ;Person p4 = Person(16 , "xx" ); cout <<endl ;Person *p5 = new Person(); cout <<endl ;Person *p6 = new Person(14 , "yy" );
VS 快捷键 1 2 多行注释:Ctrl+K+C(先按ctrl,再按K,最后按C) 取消多行注释:Ctrl+K+U(先按ctrl,再按K,最后按U)