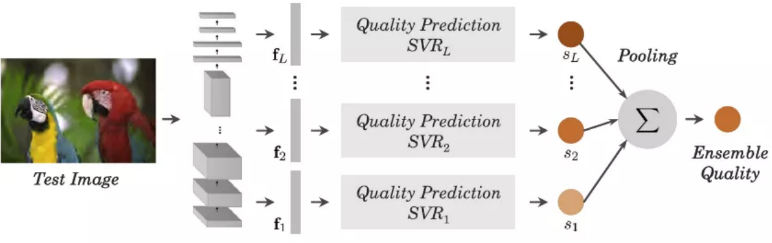
BUG Analysis
undefined reference to
编译链接错误,
新增的.cpp没有加入makefile
没有指定对应的库(.o/.a/.so)
连接库参数的顺序不对 在默认情况下,对于-l 使用库的要求是越是基础的库越要写在后面,无论是静态还动态
gcc/ld 版本不匹配 gcc/ld的版本的兼容性问题,由于gcc2 到 gcc3大版本的兼容性存在问题(其实gcc3.2到3.4也一定程度上存在这样的问题) 当在高版本机器上使用低版本的机器就会导致这样的错误, 这个问题比较常见在32位的环境上, 另外就在32位环境不小心使用了64位的库或者反过来64位环境使用了32位的库.
C/C++相互依赖和链接 gcc和g++编译结果的混用需要保证能够extern “C” 两边都可以使用的接口,在我们的64位环境中gcc链接g++的库还需要加上 -lstdc++,具体见前文对于混合编译的说明
运行期报错 这个问题基本上是由于程序使用了dlopen方式载入.so, 但.so没有把所有需要的库都链接上,具体参加上文中对于静态库和动态库混合使用的说明
Linux进程分析
https://blog.csdn.net/ktigerhero3/article/details/80004315
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1701569
手动释放Linux内存https://www.cnblogs.com/jackhub/p/3736877.html
https://blog.csdn.net/wwd0501/article/details/100041808
https://blog.csdn.net/shuihupo/article/details/80905641
contab定时任务
https://www.cnblogs.com/aminxu/p/5993769.html
coredump
SIGNAL
1 | man 7 signal |
Linux supports the standard signals listed below. Several signal numbers are architecture-dependent, as indicated in the “Value” column. (Where three values are given, the first one is usually valid for alpha and sparc, the
middle one for x86, arm, and most other architectures, and the last one for mips. (Values for parisc are not shown; see the Linux kernel source for signal numbering on that architecture.) A dash (-) denotes that a signal is
absent on the corresponding architecture.
First the signals described in the original POSIX.1-1990 standard.
Signal Value Action Comment
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
SIGHUP 1 Term Hangup detected on controlling terminal
or death of controlling process
SIGINT 2 Term Interrupt from keyboard
SIGQUIT 3 Core Quit from keyboard
SIGILL 4 Core Illegal Instruction
SIGABRT 6 Core Abort signal from abort(3)
SIGFPE 8 Core Floating-point exception
SIGKILL 9 Term Kill signal
SIGSEGV 11 Core Invalid memory reference
SIGPIPE 13 Term Broken pipe: write to pipe with no
readers; see pipe(7)
SIGALRM 14 Term Timer signal from alarm(2)
SIGTERM 15 Term Termination signal
SIGUSR1 30,10,16 Term User-defined signal 1
SIGUSR2 31,12,17 Term User-defined signal 2
SIGCHLD 20,17,18 Ign Child stopped or terminated
SIGCONT 19,18,25 Cont Continue if stopped
SIGSTOP 17,19,23 Stop Stop process
SIGTSTP 18,20,24 Stop Stop typed at terminal
SIGTTIN 21,21,26 Stop Terminal input for background process
SIGTTOU 22,22,27 Stop Terminal output for background process
The signals SIGKILL and SIGSTOP cannot be caught, blocked, or ignored.
ref: https://blog.csdn.net/wanxuexiang/article/details/88382733
dmesg
1 | dmesg |
gdb调试
1 | r |
1 | bt |
LOGS:
问题:torch cudnn Destory ini.c:138 Backtrace stopped: frame did not
1 | (gdb) bt |
解决:
SO库ld加载torch.so
主程序不需要再次ld了,不然就会上面报错
问题C++】symbol lookup error :undefined reference to找不到
解决:
1、import *.h文件 没有声明定义
2、声明定义的函数参数定义与cpp实现不一致,比如参数多了const的修饰(编译可以通过)
Debug
core dump 生成
1 调试
1 | gdb exe_file core-file |
2、bt 查看
1 | (gdb) bt |
3 查看出错的栈信息
frame + (gdb) info args
1 | (gdb) frame |
4 查看参数数据
已知cards是一个数组(17位)
1 | (gdb) print cards |
 \
\