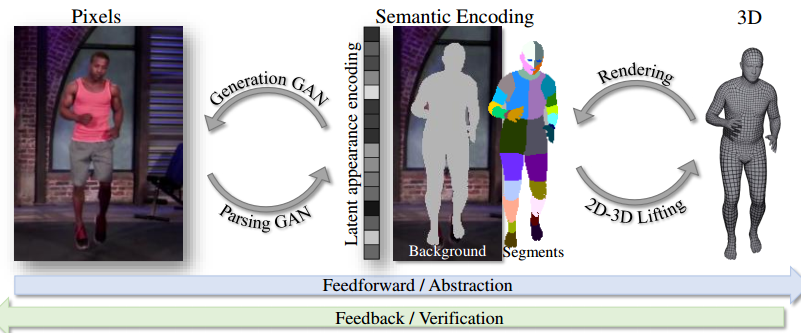
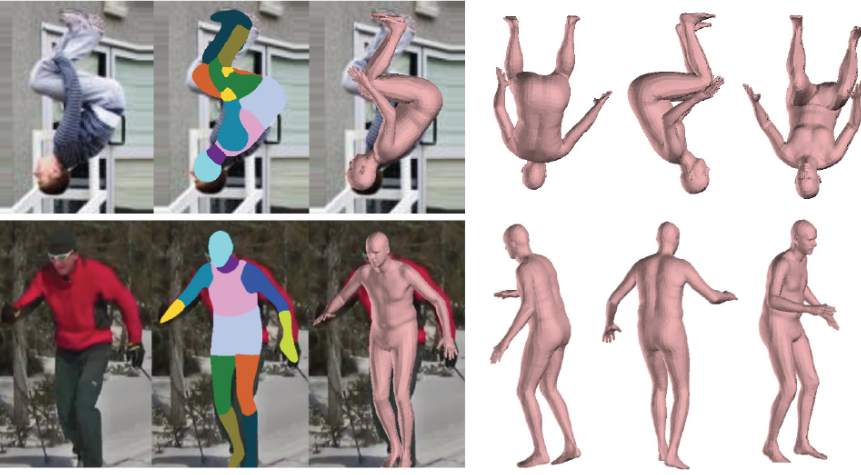
[TOC]
3D Body Model reStructure
SMPLify
SMPLR
SMPL-X

MIP-virtualhumans
http://virtualhumans.mpi-inf.mpg.de/publications.html
[CVPR, 2020] 3D Shape Restruction:

Julian Chibane, Thiemo Alldieck, Gerard Pons-Moll
Implicit Functions in Feature Space for 3D Shape Reconstruction and Completion
in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020.
BibTeX PDF
[CVPR,2020] 3D Human Texture (mir-pix-suf)

Aymen Mir, Thiemo Alldieck, Gerard Pons-Moll
Learning to Transfer Texture from Clothing Images to 3D Humans
in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020.
BibTeX PDF
[CVPR,2020] VTailor
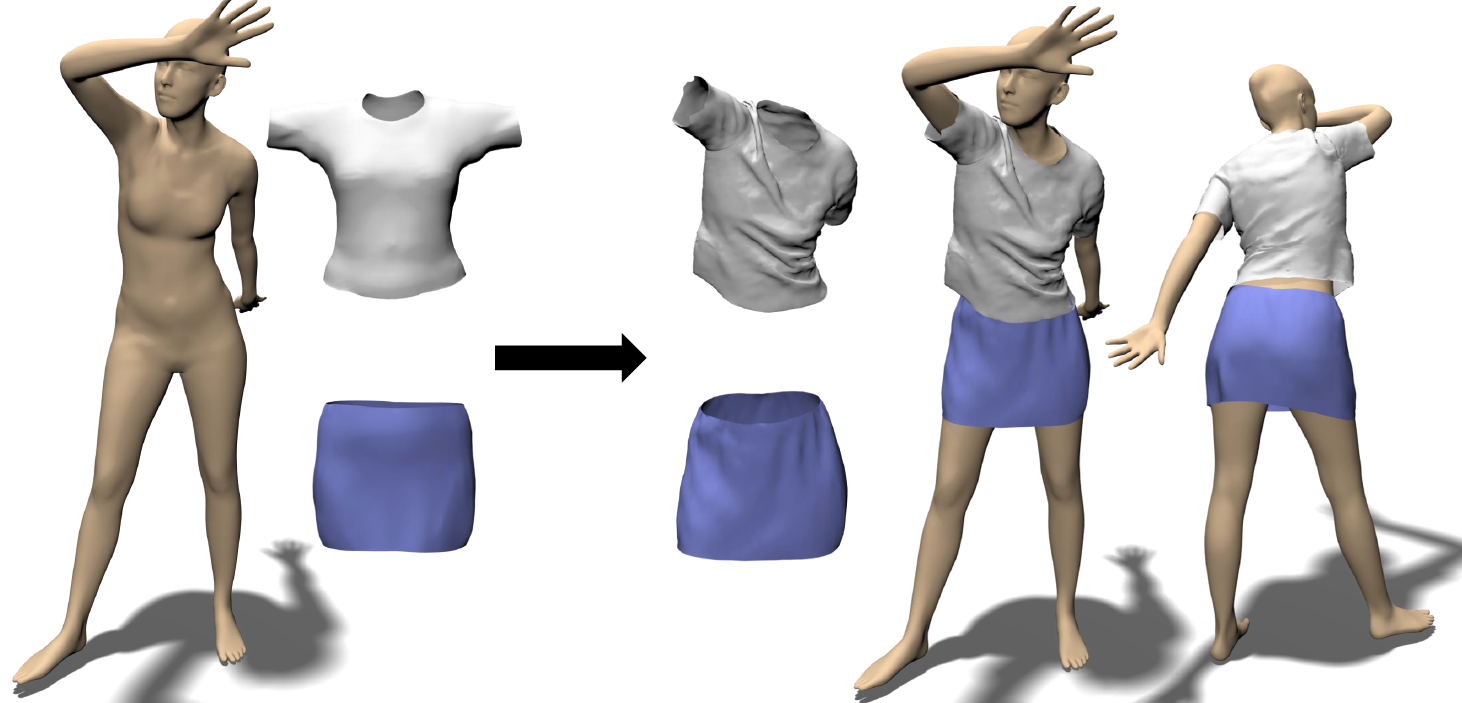
Chaitanya Patel, Zhouyingcheng Liao, Gerard Pons-Moll
The Virtual Tailor: Predicting Clothing in 3D as a Function of Human Pose, Shape and Garment Style
in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020.
BibTeX PDF
[CVPR,2020] Drees3DPeople
- CAPE model
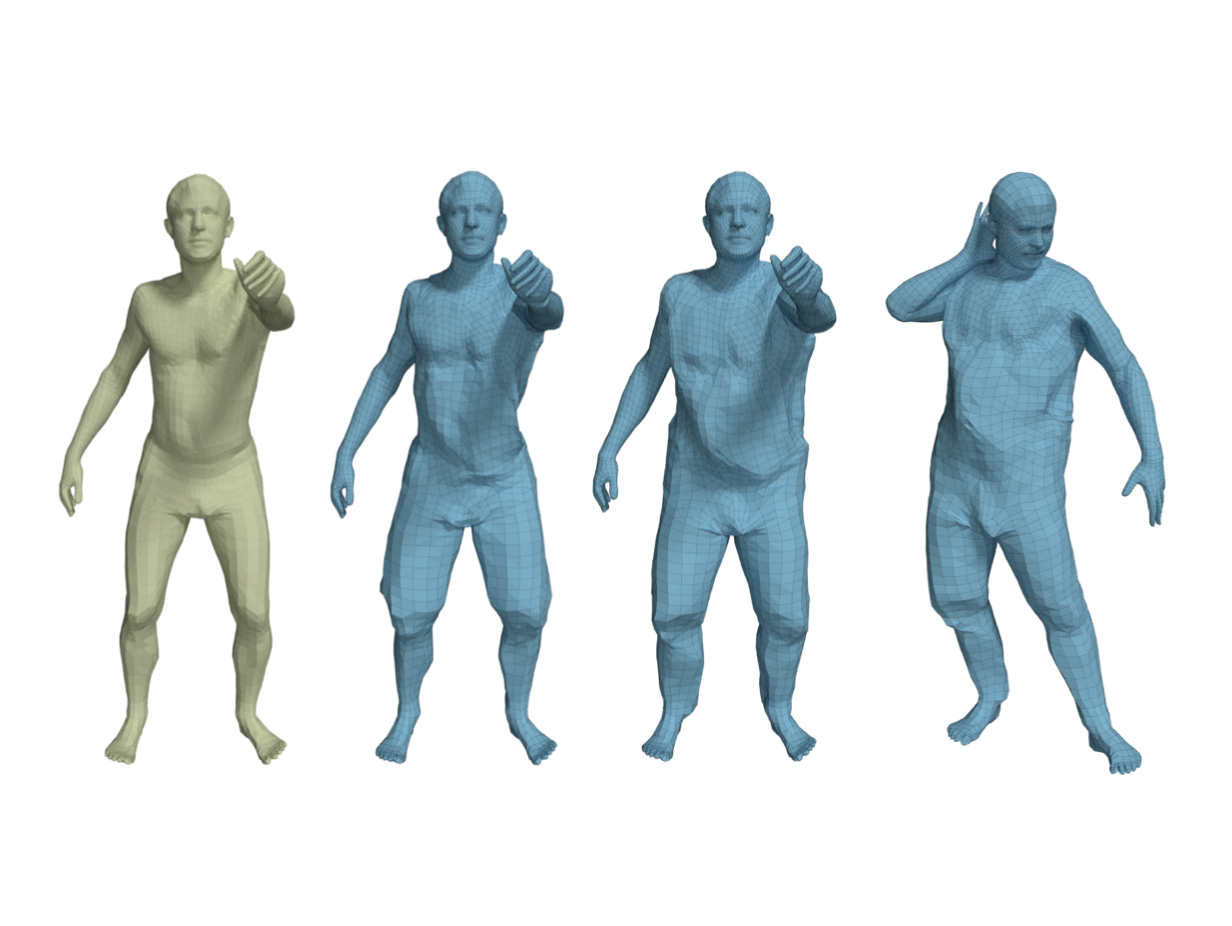
Qianli Ma, Jinlong Yang, Anurag Ranjan, Sergi Pujades, Gerard Pons-Moll, Siyu Tang, Michael Black
Learning to Dress 3D People in Generative Clothing
学习给3D人物穿上生成性服装
in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020.
BibTeX arXiv
- 模型穿衣(无纹理效果)
[CVPR,2020] DeepCap

Marc Habermann, Weipeng Xu, Michael and Zollhoefer, Gerard Pons-Moll, Christian Theobalt
DeepCap: Monocular Human Performance Capture Using Weak Supervision
in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020.
BibTeX
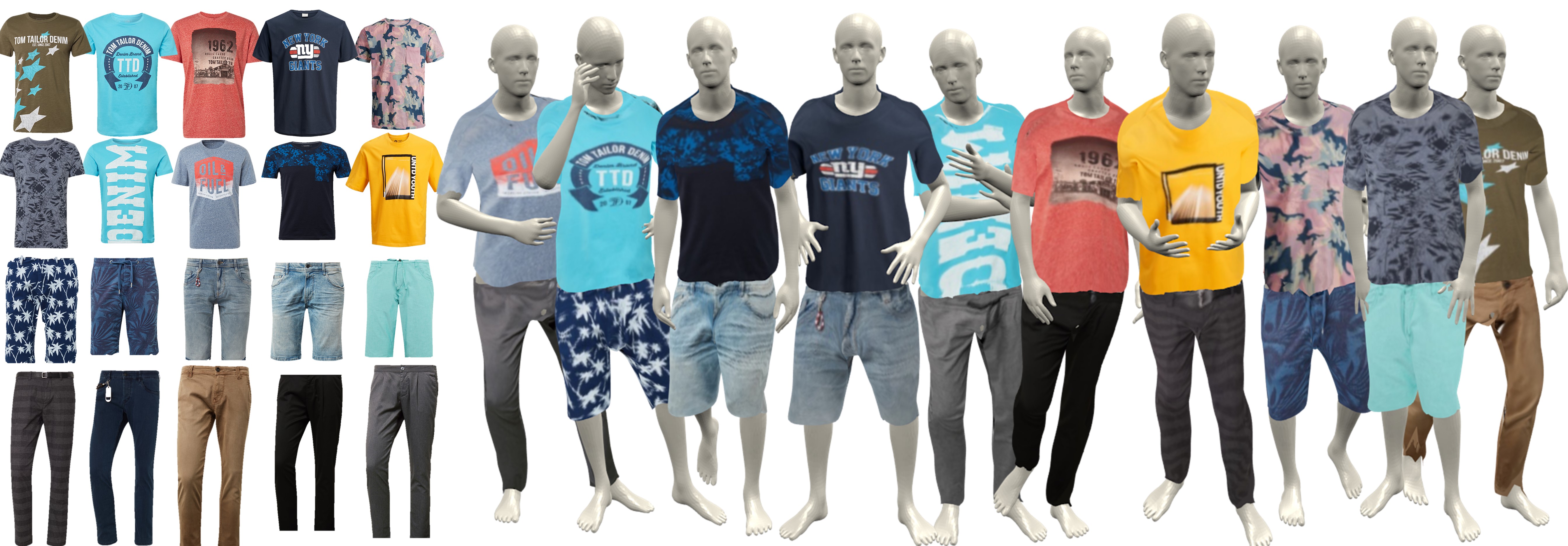
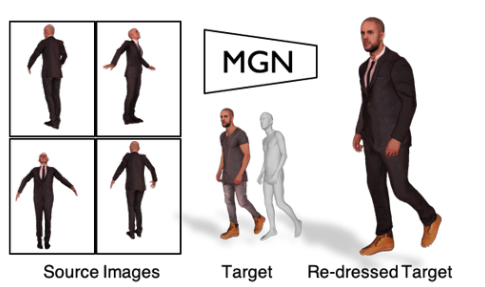
[ICCV,2019] MGN
- 1-8 Image
标题:Multi-Garment Net: Learning to Dress 3D People from Images
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.06903
代码:https://github.com/bharat-b7/MultiGarmentNetwork
- ⭐⭐⭐⭐
作者:B. L. Bhatnagar
马克斯普朗克信息学院,萨尔兰信息学院,德国
专门研究REAL VIRTUAL HUMANS http://virtualhumans.mpi-inf.mpg.de/
学习从图像中为3D人物穿衣
基于SMPL,提出MGN网络,用于从视频帧中预测体型和服装的方法。
Garment Registration:
Laplacian Mesh Processing 三维网格拉普拉斯处理
We register the scans using multi-mesh registration
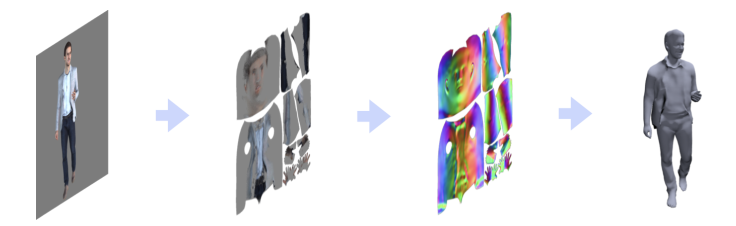
[ICCV,2019] Tex2Shape
作者:Thiemo Alldieck, Gerard Pons-Moll, Christian Theobalt, Marcus Magnor:
论文:Tex2Shape: Detailed Full Human Body Geometry from a Single Image
GitHub:https://github.com/thmoa/tex2shape
Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.08645
单张图片—人体3D建模(无纹理重建)
- 形状回归—-转化—->图像到图像的对齐翻译问题
输入:现成方法得到的可见部分的纹理
[ICCV,2019] AMASS
Naureen Mahmood, Nima Ghorbani, Nikolaus F. Troje, Gerard Pons-Moll, Michael J. Black
AMASS: Archive of Motion Capture as Surface Shapes
AMASS 作为曲面形状的运动捕捉存档
in IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2019

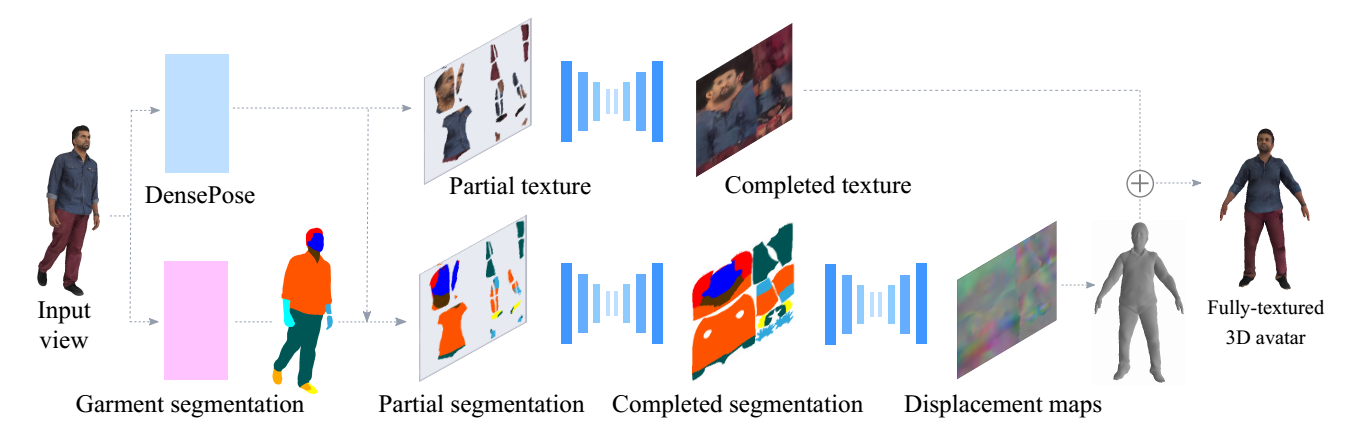
[3DV, 2019] 360tex
Verica Lazova, Eldar Insafutdinov, Gerard Pons-Moll
360-Degree Textures of People in Clothing from a Single Image
in International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), 2019.
源码: http://virtualhumans.mpi-inf.mpg.de/360tex/
从1张图片生成3D穿衣人物(带纹理)
在本文中,我们从一个单一的图像预测一个人的完整的3D化身。我们使用图像到图像的转换方法来推断SMPL模型的uv空间中的纹理和几何体。在给定输入视图的局部纹理和分割布局图的情况下,我们的模型预测了完整的分割图、完整的纹理图和位移图。预测出的地图可以应用到SMPL模型中,以便自然地推广到新的姿势、形状,甚至新衣服。为了在一个公共的UV空间中学习我们的模型,我们将SMPL模型非刚性地注册到数千个3D扫描中,有效地将纹理和几何图形编码为对应的图像。这将困难的三维推理任务转换为更简单的图像转换任务。对DeepFashion数据集中的人物和图像的渲染扫描结果表明,我们的方法可以从单个图像中重建出可信的3D化身。我们进一步使用我们的模型来数字化地改变姿势、形状、在人与人之间交换衣服和编辑衣服。为了鼓励这方面的研究,我们将提供用于研究目的的源代码[5]。
[CVPR, 2019] Octopus
Reconstruct 3D Cloth Body –CVPR_2019
- Single Image
《Learning to Reconstruct People in Clothing From a Single RGB Camera》
8张照片生成3D模型
作者:T. Alldieck, M. A. Magnor, B. L. Bhatnagar, C. Theobalt and G. Pons-Moll
代码:https://github.com/thmoa/octopus
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.05885

dataset
purchased 163 scans from renderpeople.com
purchased 54 from axyzdesign.com.
1826 scans were kindly provided from Twindom (https://web.twindom.com/).
PGN: 转换数据
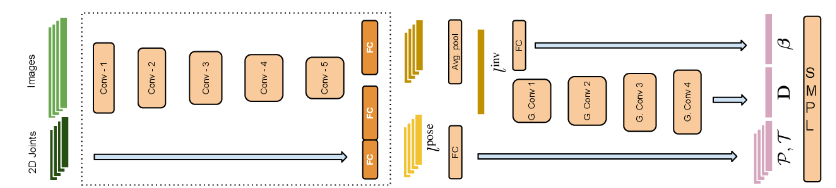
网络结构:
Generating 3D faces using convolutional mesh autoencoders.
纹理计算参考:
Detailed human avatars from monocular video.
steps:
Rendering
segmentation
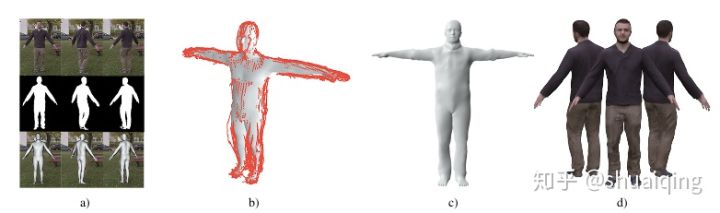
[3DV, 2018.8] [Detailed Human Avatars from Monocular Video]
(a). estimate a medium level body shape based on segmentations (基于语义分割的中等级别的身体形状)
(b). we add details using shape-from-shading.(Body Shape细节的优化)
(c). Finally we compute a texture using a semantic prior (c) [ a novel graph cut optimization strategy]
问题: 如何从RGB视频中获取细致的人体模型
输入: 单人的单目视频+轮廓信息+语义分割
输出: 基于SMPL的更细致的人体模型
和之前的区别是,
- 增加shape-from-shading方法,
- 对SMPL模型进行了划分,增加其点的数量与面片的数量
- 贴纹理用了graph cut优化
代码:
纹理拼接代码semantic human texture stitching
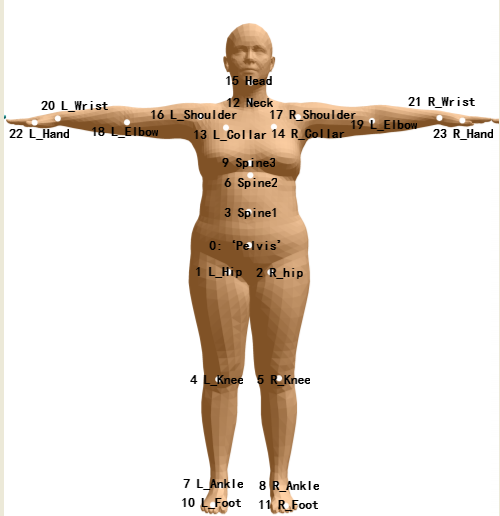
基于SMPL的p,$\theta$新增了W(混合皮肤)
skeleton joints J(β)
标准T-Pose
consists of N = 110210 vertices and F = 220416 faces.
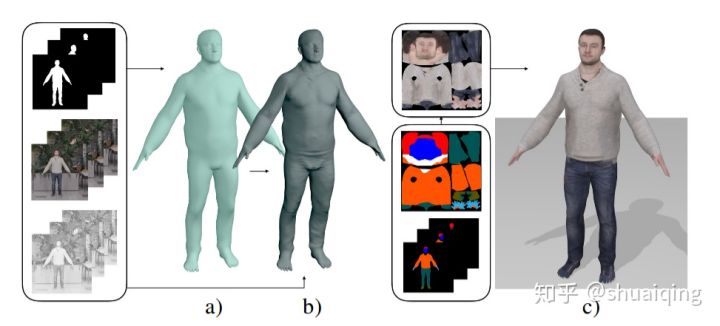
[CVPR, 2018.3] [Video Based Reconstruction of 3D People Models]
calculate poses using the SMPL model (a)
unpose silhouette camera rays (unposed silhouettes depicted in red) unpose轮廓相机射线
optimize for the subjects shape in the canonical T-pose (c) 优化的对象形状,以规范T-pose形式 (c)
calculate a texture and generate a personalized blend shape model (d) 计算纹理和生成混合形状模型
问题: 如何从RGB视频中获取细致的人体模型
输入: 单人的单目视频+轮廓
输出: 基于SMPL的细致的人体模型
https://graphics.tu-bs.de/people-snapshot
- github code
- dataset
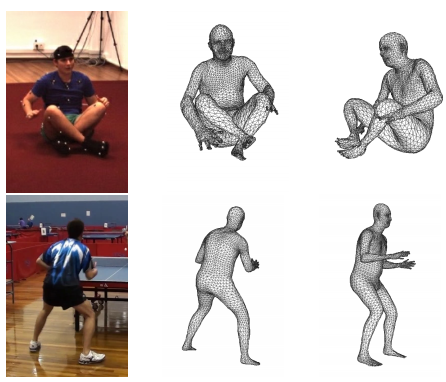
[ECCV,2018]VRN-Body
《3D Human Body Reconstruction from a Single Image via Volumetric Regression》
- ⭐⭐⭐
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1809.03770v1.pdf
1 | A.S. Jackson [](https://aaronsplace.co.uk/) 英国诺丁汉大学计算机视觉实验室 研究员 -- 图像深度学习 |
- 3D Human Body Reconstruction
- 3D Texture 复原:效果一般,人物恢复模糊。

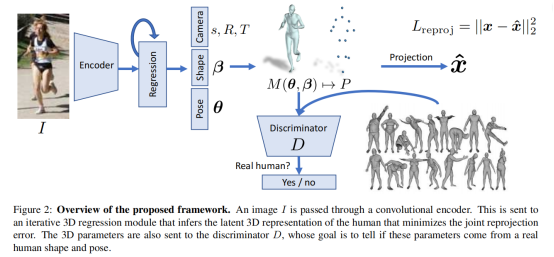
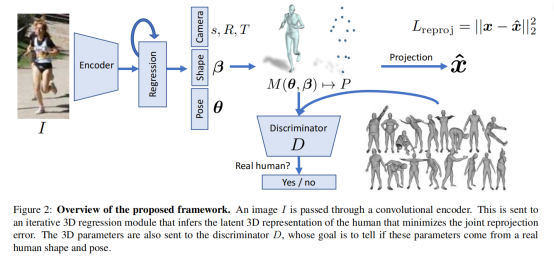
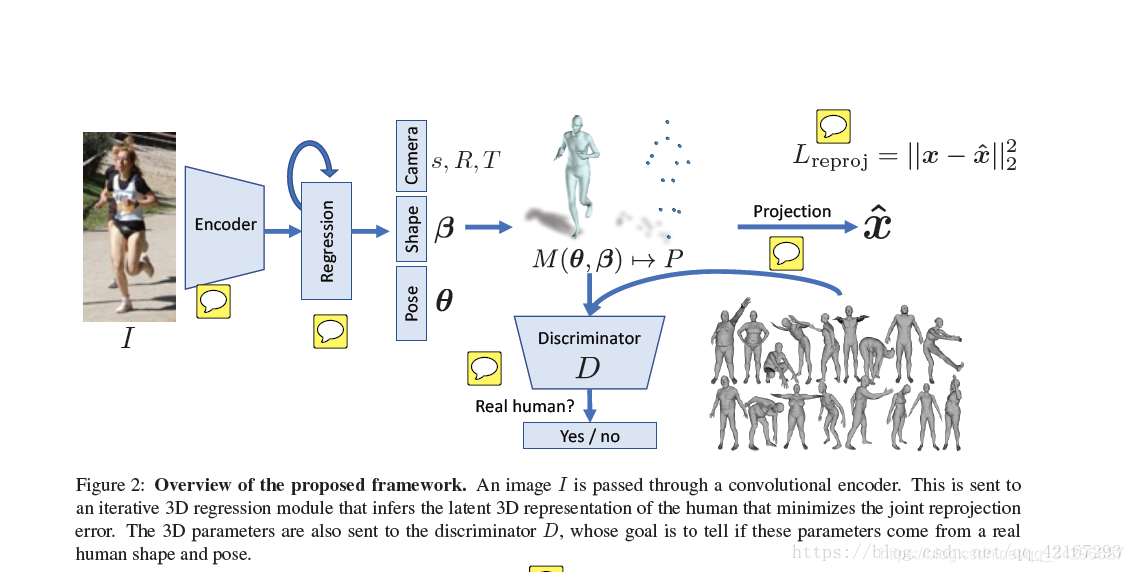
[2017] HMR
End to end recovery of human shape and pose: 201712
[2019] MTC
https://new.qq.com/omn/20200908/20200908A09RJD00.html
[2020] FrankMocap
科学怪物!3D人体全身运动捕捉系统,港中文联合Facebook出品
https://new.qq.com/omn/20200908/20200908A09RJD00.html
使用神经网络拟合smplx的人体参数,手部参数,极大的提升了原本SMPLify-x的运算效率
official web site introduction

基础知识SMPL:
| SMPL | N = 6890 vertices and F = 13776 faces. | |
| video2mesh | ||
| Video Reconstruct | 穿裙子解决不了 改变不了smpl model的拓扑结构 拉不过去 | |
| Video Avatars—v1 | <Video based reconstruction of 3D people models> 贴图方法: | 同一个作者 |
| VideoAvatars-v2 | 同一个作者 | |
| Octopus | octopus 有模型 有纹理贴图 用了Detailed Human Avatars from Monocular Video.的贴图方法 | 2019.4video2mesh延伸论文,同一实验室 |
| Tex2Shape | N = 27554 vertices and F = 55104 faces | |
| MGN | V = 27554 VT+V = 29193 F = 54831 |
Video Avatar重建(同一作者)
《1803 Video based reconstruction of 3D people models》
- 我们的主要贡献是在一个共同的参考系中,将对应于动态人体轮廓的轮廓锥变换成视觉外壳。
《1808 Detailed Human Avatars from Monocular Video.》 consists of N = 110210 vertices and F = 220416 faces.
1803:
pose reconstruction (Sec. 3.2)
consensus shape estimation (Sec. 3.3)
frame refinement and texture map generation (Sec. 3.4).
Our main contribution is step 2), the consensus shape estimation;
step 1) builds on previous work and step 3) to obtain texture and time-varying details is optional
基础知识CV
Non-rigid surface deformations 非刚性表面变形:
非刚性变形的思想是:皮肤变形,不是由单一骨骼的运动来控制,而是由许多骨头的共同运作的结果来支配。